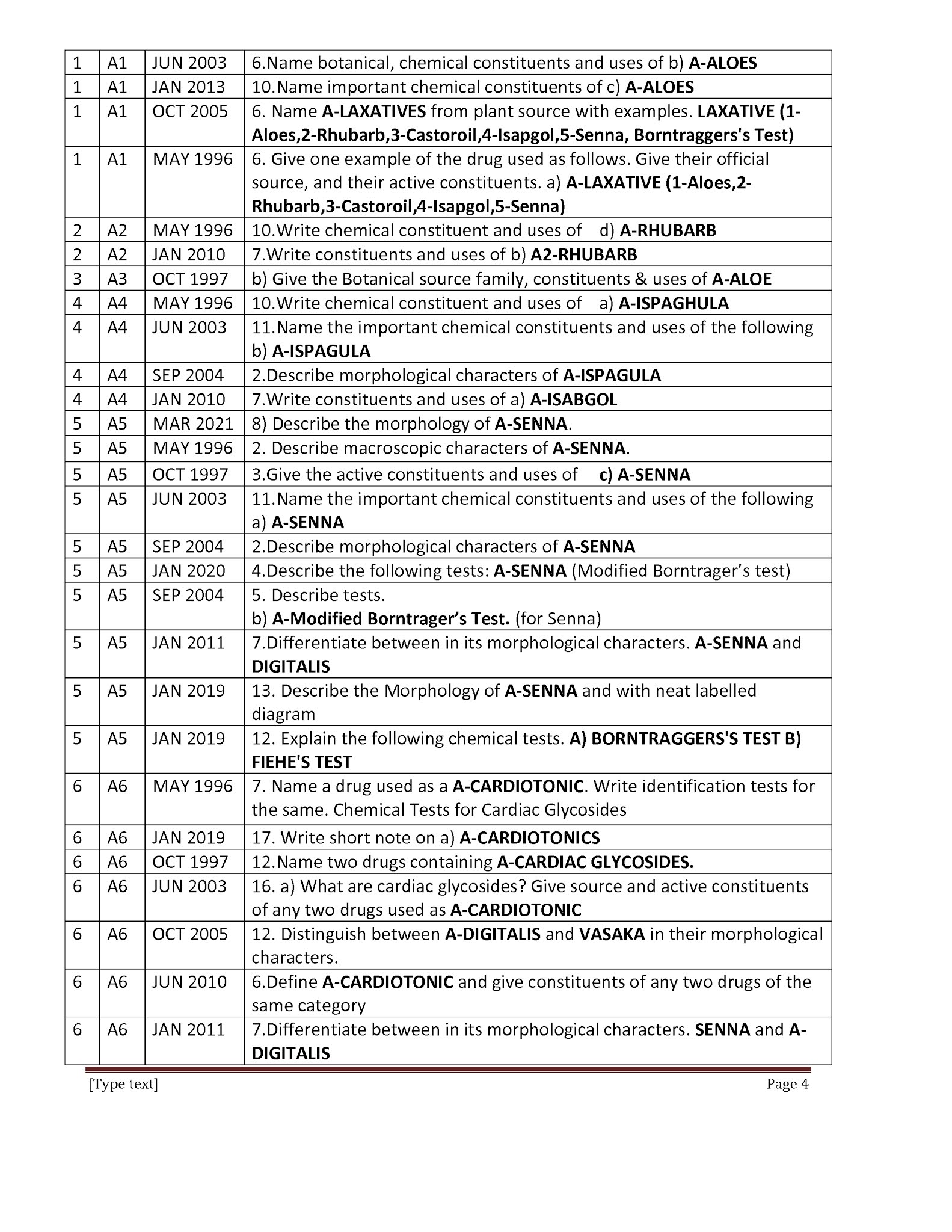
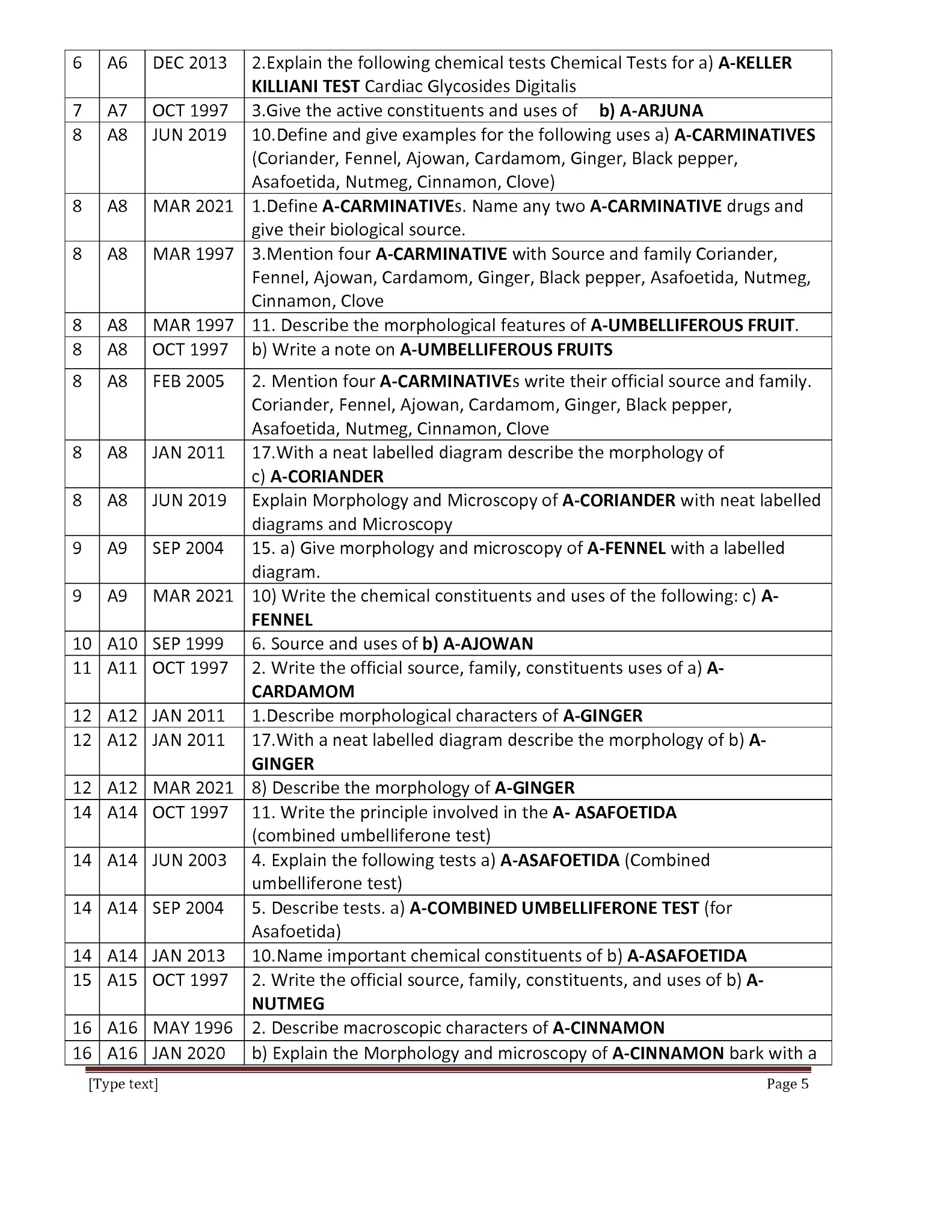
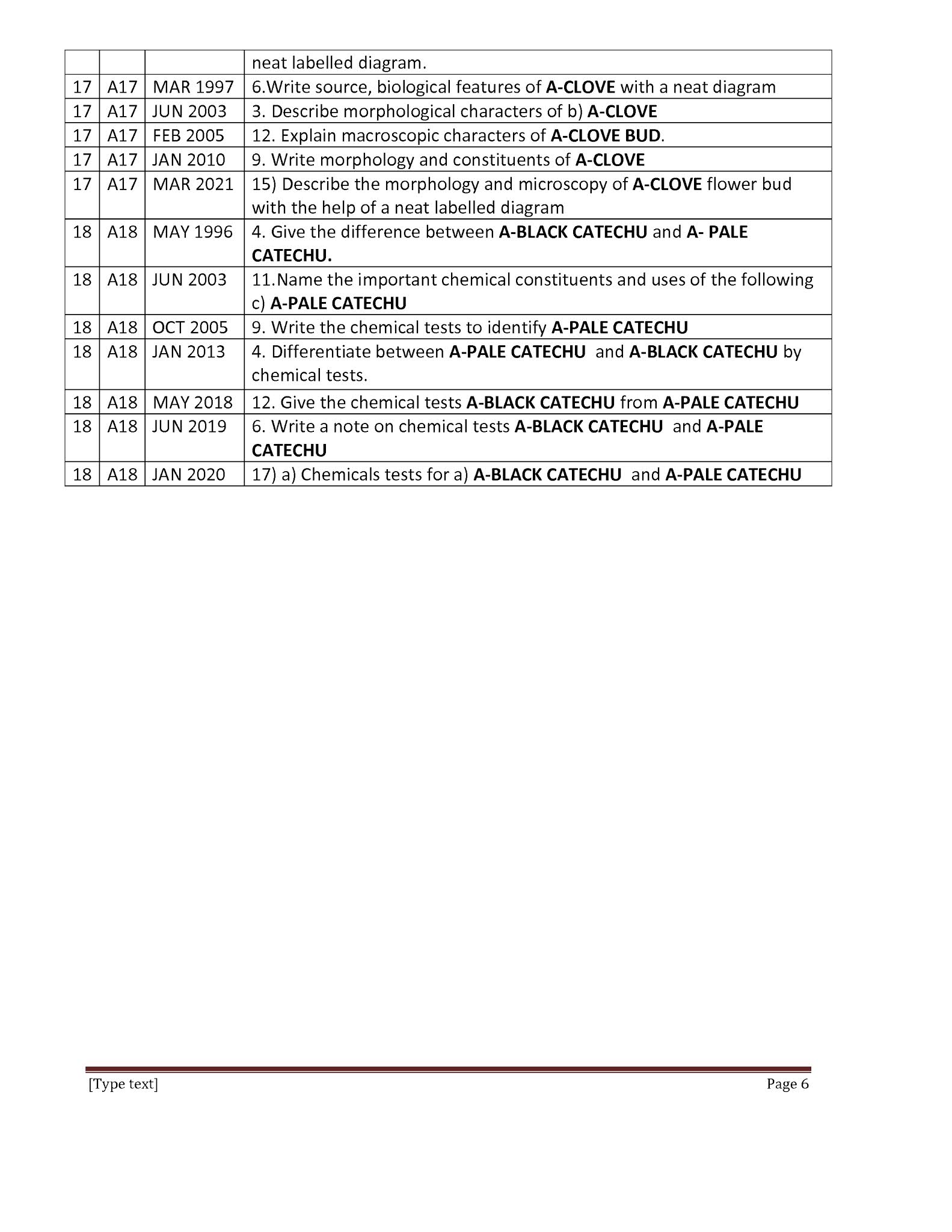
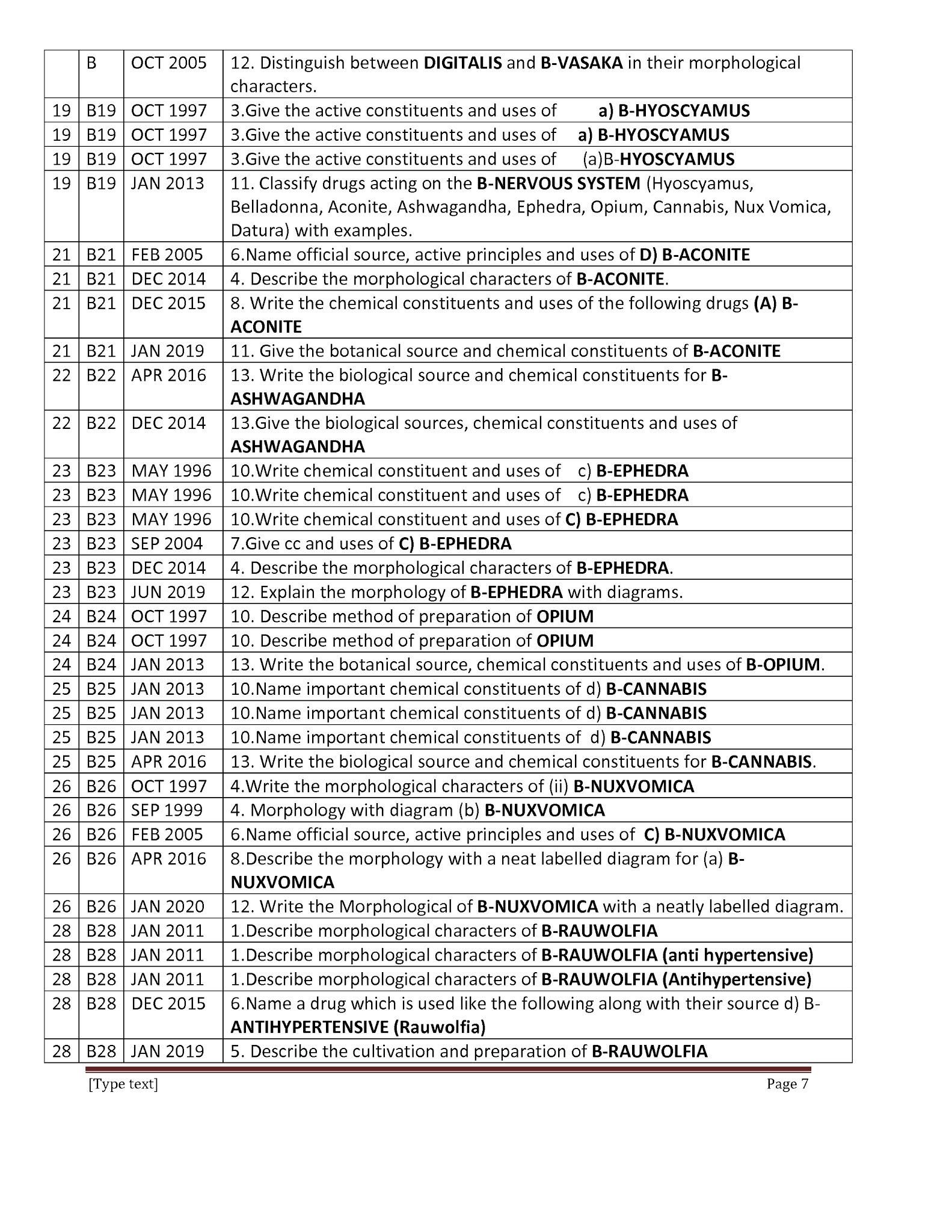
Phyto Chemicals
D. Pharm Notes, Herbal healer treating Uterine prolapse and Ayurveda Treatment.
ER 2020 Pharmacognosy: CHAPTER 1. Definition, history, present status and scope of Pharmacognosy 2 Hours
CHAPTER 1. Definition, history, present status and scope of Pharmacognosy 2Hrs
MEANING or DEFINITION OF PHARMACOGNOSY
>Pharmacognosy, known initially as materia medica, defined as the study of crude drugs obtained from plants, animals and mineral kingdom and their constituents.
>There is historical misinformation about who created the term pharmacognosy. According to some sources, it was C. A. Seydler, a medical student at Halle, Germany, in 1815; he wrote his doctoral thesis titled Analectica Pharmacognostica.
>However, recent historical research has found an earlier usage of this term. The physician J. A. Schmidt (Vienna) used that one in his Lehrbuch der materia medica in 1811, to describe the study of medicinal plants and their properties.
>They derive the word pharmacognosy from two Latin words Pharmakon, ‘a drug,’ and Gignoso, ‘to gain a knowledge of ’. It means ‘knowledge or science of drugs’.
History of Pharmacognosy
→We can regard > History of Pharmacognosy as a history of Pharmacy and medicine because pharmacognosy had its origin in health-related activities of the most primitive human race of the remote past.
→ In the early period, primitive men went in search of food and ate at random, plants or their parts like leaves, fruits, etc.
→ As they observed no harmful effects, they considered them as edible materials and used them as food.
→ Observing other effects, they started using them as medicine or as defence instruments, e.g. poisonous and death arrow poison. Trial and error got this knowledge.
→ It is probable that by a combination of these various methods, ancient people could build up a considerable knowledge of medicinal and food plants.
→ They transmitted gained knowledge from generation to generation and new information to it.
→ A group of people in each generation started specialising in collecting and processing medicinal plants and using them against various diseases.
→Before people could read and write, they passed the knowledge of drugs from one generation to another either orally or by the use of some signs and symbols.
→ As far as historical records are available, the Chinese pharmacy stems from Shen Nung (2700 B.C) who investigated the medicinal value of several hundred herbs and had Pen T-sao recording 365 drugs. The most important clinical manual of Traditional Chinese Zhang Han lun (Treatise on the treatment of acute diseases caused by cold).
→ From the Sung Dynasty (960-1276) the establishment of the pharmaceutical system has been a Standard practice throughout the country.
→ In 1552, during the later Ming Dynasty, Li Shi Zhen (1548-1593) began work on the monumental Pen Ts'ao, Kan Kan Mu (Herbal with commentary). This listed 1892 drugs, 376 described for the first time with 1160 drawings.
→ Ancient Egypt witnessed the most complete medical documents Ebers Papyrus, a collection of 800 prescriptions, mentioning 700 drugs and Edwin Smith Papyrus, containing surgical instructions and formulas for cosmetics.
→ Kahun Medical Papyrus is the oldest document - comes from 1900 BC and deals with the health of women, including birth and instructions.
→ Many of the present day important drugs like Henbane, Opium pomegranate, castor oil, aloe, onion and many others were in common use in Egypt about 4500 years ago.
→They described the earliest plant medicines used in the Ayurvedic system around 1200 BC with a list of 127 plants.
→ They divided the Ayurvedic writing into three main scripts-Charaka Samhita, Sushruta Samhita, Astanga Hridaya Samhita.
→The practice of medicine using medicinal plants flourished most during Greek civilisation when many historical personalities practised herbal medicines.
→Some of the early naturalists, scientists and physicians who contributed enormously to the development of human knowledge about medicinal plants, including Hippocrates (460-370 BC) Aristotle (384-322 BC) Theophrastus (370-287 BC) Dioscorides Pling and Galen (131-200 AD)
→They regarded →Hippocrates as the father of medicine for his contribution to human anatomy and physiology. Also known to have collected and identified several medicinal plants. And practised herbal medicine.
→His materia medica comprises some 300 to 400 medicinal plants.
→ Aristotle recorded the properties of over 500 plants of medicinal importance.
→Dioscorides published five volumes of the book, entitled ' De Materia Medica' in 78 AD. This described over 600 medicinal plants.
→Galen, for the first time in history, described hundreds of recipes and formulations of medicinal preparations containing both plant and animal ingredients.
→The present day Galenical pharmacy is a manifestation of his methods and recipes.
→Present day allopathic and homoeopathic systems of medicine on the doctrines expatiate by Galen.
→In earlier days, the apothecary (Pharmacist -physician) used to handle the works of both the pharmacist and physicians.
PRESENT STATUS OF PHARMACOGNOSY:
In times of yore, pharmacognosy was considered as the study of drugs of natural origin.
The Pharmacognosy derived it as the study of physical, chemical, biochemical and biological properties of drug, drug substances or potential drugs or drug substances of natural origin as well as the search for new drugs from natural sources.
The world of pharmacognosy has continuously been enriching with multifaceted information considering various aspects of the natural drugs including history, alternative medicinal systems, classification, morphology, identification, cultivation, collection, extraction, isolation and purification of herbal drugs and modern plant biotechnology production and utilisation of drugs;
trade and utilisation of medicinal and aromatic plants and their contribution to the national economy; adulteration of drugs of natural origin; evaluation of drugs by their physical, chemical and organoleptic properties; biological screening of herbal drugs;
Biosynthetic pathways of various phytochemicals. emphasises the biodiversity of plants and encompasses biosynthesis, extraction, isolation of compounds with TLC identification, bioactivity determination and synthesis of plant components of interest in addition to the traditional pharmacognosy comprising cultivation, collection, morphology, microscopy, taxonomy, chemical constituents and uses of drugs of natural origin.
Such enormous information about the natural drug gives rise to a subject that is now recognized as modern pharmacognosy.
Pharmacognosy is a highly interdisciplinary science, encompassing a broad range of studies involving phytochemical study of medicinal plants and biologically active principles obtained from plants in addition to the traditional pharmacognostical aspects of natural drugs.
Syllabus ER2020 I D. Pharm PHARMACOGNOSY - THEORY and Practicals
PHARMACOGNOSY - THEORY
Course Code: ER20-137 75
Hours (3 Hours/week)
Scope: This course is designed to impart knowledge on the medicinal uses of various drugs of natural origin. Also, the course emphasises the fundamental concepts in the evaluation of crude drugs, alternative systems of medicine, nutraceuticals, and herbal cosmetics.
Course Objectives: This course will discuss the following aspects of drug substances derived from natural resources.
1. Occurrence, distribution, isolation, identification tests of common phytoconstituents.
2. Therapeutic activity and pharmaceutical applications of various natural drug substances and phytoconstituents.
3. Biological source, chemical constituents of selected crude drugs and their therapeutic efficacy in common diseases and ailments.
4. Basic concepts in quality control of crude drugs and various system of medicines.
5. Applications of herbs in health foods and cosmetics Course Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, the students will be able to
identify the important/common crude drugs of natural origin
Describe the uses of herbs in nutraceuticals and cosmeceuticals
Discuss the principles of alternative system of medicines
Describe the importance of quality control of drugs of natural origin.
Chapter Topic Hours
CHAPTER 1. Definition, history, present status and scope of Pharmacognosy 2Hrs
Classification of drugs:
Alphabetical
Taxonomical
Morphological
Pharmacological
Chemical
Chemo-taxonomical 4Hrs
Quality control of crude drugs: o Different methods of adulteration of crude drugs o Evaluation of crude drugs. 6Hrs.
Brief outline of occurrence, distribution, isolation, identification tests, therapeutic activity and pharmaceutical applications of alkaloids, terpenoids, glycosides, volatile oils, tannins and resins. 6Hrs.
Biological source, chemical constituents and therapeutic efficacy of the following categories of crude drugs. 30Hrs.
Laxatives: Aloe, Castor oil, ispaghula, Senna
Cardiotonic: Digitalis, Arjuna
Carminatives and G.l. regulators: Coriander, Fennel, Cardamom, Ginger, Clove, Black Pepper, Asafoetida, Nutmeg, Cinnamon.
Astringents: Myrobalan, Black Catechu, Pale Catechu
Drugs acting on nervous system: Hyoscyamus, Belladonna, Ephedra, Opium, Tea leaves,
Coffee seeds, Coca.
Anti-hypertensive: Rauwolfia
Antitussive: Vasaka, Tolu Balsam
Anti-rheumatics: Colchicum seed
Anti-tumour: Vinca, Podophyllum
Antidiabetics: Pterocarpus, Gymnema
Diuretics: Gokhru, Punarnava
Antidysenteric ipecacuanha
Antiseptics and disinfectants: Benzoin, Myrrh, Neem, Turmeric
Antimalarials: Cinchona, Artemisia
Oxytocic: Ergot
Vitamins: Cod liver oil, Shark liver oil
Enzymes: Papaya, Diastase, Pancreatin, Yeast
Pharmaceutical Aids: Kaolin, Lanolin, Beeswax, Acacia, Tragacanth, Sodium alginate, Agar,
Guar gum, Gelatine.
Miscellaneous Squill, Galls, Ashwagandha, Tulsi, Guggul.
Plant fibres used as surgical dressings: Cotton, silk, wool and regenerated fibres
Sutures - Surgical Catgut and Ligatures. 3Hrs.
Basic principles involved in the traditional systems of medicine like: Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani and Homoeopathy o Method of preparation of Ayurvedic formulations like: Arista, Asava, Gutika, Taila, Churna, Lehya and Bhasma 8Hrs.
Role of medicinal and aromatic plants in national economy and their export potential 2Hrs.
Herbs as health food: Brief introduction and therapeutic applications of:
Nutraceuticals, Antioxidants, Probiotics, Probiotics, Dietary fibres, Omega-3-fatty acids, Spirulina, Carotenoids, Soya and Garlic. 4Hrs.
introduction to herbal formulations 4Hrs.
Herbal cosmetics: Sources, chemical constituents, commercial preparations,
therapeutic and cosmetic uses of: Aloe vera gel, Almond oil, Lavender oil, Olive oil, Rosemary oil, SandalWood oil. 4Hrs.
Phytochemical investigation of drugs 2Hrs.
PHARMACOGNOSY - PRACTICAL
Course Code: ER20-13P
75 Hours (3 Hours/week)
Scope: This course is designed to train the students in physical identification, morphological characterization, physical and chemical characterization, and evaluation of commonly used herbal drugs. Course Objectives: This course will provide hands-on experiences to the students in
1. identification of the crude drugs based on their morphological characteristics
2. Various characteristic anatomical characteristics of the herbal drugs studied
through the transverse section.
3. Physical and chemical tests to evaluate the crude drugs Course Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, the students will be able to
Identify the given crude drugs based on the morphological characteristics.
Take a transverse section of the given crude drugs.
Describe the anatomical characteristics of the given crude drug under
microscopical conditions.
Carry out the physical and chemical tests to evaluate the given crude drugs.
Morphological identification of the following drugs: ispaghula, Senna, Coriander, Fennel, Cardamom, Ginger, Nutmeg, Black Pepper, Cinnamon, Clove, Ephedra, Rauwolfia, Gokhru, Punarnava, Cinchona, Agar.
Gross anatomical studies (Transverse Section) of the following drugs: Ajwain, Datura, Cinnamon, Cinchona, Coriander, Ashwagandha, Liquorice, Clove, Curcuma, Nux-vomica, Vasaka
Physical and chemical tests for evaluation of any FIVE of the following drugs:
Asafoetida,
Benzoin,
Pale catechu,
Black catechu,
Castor oil,
Acacia,
Tragacanth,
Agar,
Guar gum,
Gelatine.
Assignments: The students shall be asked to submit the written assignments on the following topics (One assignment per student per sessional period. i.e., a minimum of THREE assignments per student)
1. Market preparations of various dosage forms of Ayurvedic, Unani, Siddha, Homoeopathic (Classical and Proprietary), indications, and their labelling requirements.
2. Market preparations of various herbal formulations and herbal cosmetics, indications, and their labelling requirements.
3. Herb-Drug interactions documented in the literature and their clinical significance.
Field Visit: The students shall be taken in groups to a medicinal garden to witness and understand the nature of various medicinal plants discussed in theory and practical courses. Additionally, they shall be taken in groups to the pharmacies of traditional systems of medicines to understand the availability of various dosage forms and their labelling requirements. individual reports from each student on their learning experience from the field visit shall be submitted.
PHARMACOGNOSY - THEORY
Course Code: ER20-137 75
Hours (3 Hours/week)
Scope: This course imparts knowledge on the medicinal uses of various drugs of natural origin. Also, the course emphasises the fundamental concepts in the evaluation of crude drugs, alternative systems of medicine, nutraceuticals, and herbal cosmetics.
ವ್ಯಾಪ್ತಿ: ಈ ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ನೈಸರ್ಗಿಕ ಮೂಲದ ವಿವಿಧ ಔಷಧಗಳ ಔಷಧೀಯ ಉಪಯೋಗಗಳ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಜ್ಞಾನವನ್ನು ನೀಡುತ್ತದೆ. ಅಲ್ಲದೆ, ಈ ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಗಳು, ಪರ್ಯಾಯ ಔಷಧ ವ್ಯವಸ್ಥೆಗಳು, ನ್ಯೂಟ್ರಾಸಿಯುಟಿಕಲ್ಸ್ ಮತ್ತು ಗಿಡಮೂಲಿಕೆ ಸೌಂದರ್ಯವರ್ಧಕಗಳ ಮೌಲ್ಯಮಾಪನದಲ್ಲಿನ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಪರಿಕಲ್ಪನೆಗಳನ್ನು ಒತ್ತಿ ಹೇಳುತ್ತದೆ.
Course Objectives: This course will discuss the following aspects of drug substances derived from natural resources.
ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ಉದ್ದೇಶಗಳು: ಈ ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ನೈಸರ್ಗಿಕ ಸಂಪನ್ಮೂಲಗಳಿಂದ ಪಡೆದ ಔಷಧ ವಸ್ತುಗಳ ಈ ಕೆಳಗಿನ ಅಂಶಗಳನ್ನು ಚರ್ಚಿಸುತ್ತದೆ.
1. Occurrence, distribution, isolation, identification tests of common phytoconstituents.
1. ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯ ಫೈಟೋಘಟಕಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಸಂಭವಿಸುವಿಕೆ, ವಿತರಣೆ, ಪ್ರತ್ಯೇಕತೆ, ಗುರುತಿಸುವಿಕೆ ಪರೀಕ್ಷೆಗಳು.
2. Therapeutic activity and pharmaceutical applications of various natural drug substances and phytoconstituents.
2. ವಿವಿಧ ನೈಸರ್ಗಿಕ ಔಷಧ ವಸ್ತುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಫೈಟೋಘಟಕಾಂಶಗಳ ಚಿಕಿತ್ಸಕ ಚಟುವಟಿಕೆ ಮತ್ತು ಔಷಧೀಯ ಅನ್ವಯಗಳು.
3. Biological source, chemical constituents of selected crude drugs and their therapeutic efficacy in common diseases and ailments.
3. ಜೈವಿಕ ಮೂಲ, ಆಯ್ದ ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಗಳ ರಾಸಾಯನಿಕ ಘಟಕಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯ ರೋಗಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕಾಯಿಲೆಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಅವುಗಳ ಚಿಕಿತ್ಸಕ ಪರಿಣಾಮಕಾರಿತ್ವ.
4. Basic concepts in quality control of crude drugs and various systems of medicines.
4. ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ವಿವಿಧ ಔಷಧಗಳ ಗುಣಮಟ್ಟ ನಿಯಂತ್ರಣದಲ್ಲಿ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಪರಿಕಲ್ಪನೆಗಳು.
5. Applications of herbs in health foods and cosmetics Course Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, the students will be able to
5. ಆರೋಗ್ಯ ಆಹಾರಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಸೌಂದರ್ಯವರ್ಧಕಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಗಿಡಮೂಲಿಕೆಗಳ ಅನ್ವಯಗಳು ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ಫಲಿತಾಂಶಗಳು: ಈ ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ಅನ್ನು ಯಶಸ್ವಿಯಾಗಿ ಪೂರ್ಣಗೊಳಿಸಿದ ನಂತರ, ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಗಳು ಮಾಡಲು ಸಾಧ್ಯವಾಗುತ್ತದೆ
identify the important/common crude drugs of natural origin.
ನೈಸರ್ಗಿಕ ಮೂಲದ ಪ್ರಮುಖ/ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯ ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಗಳನ್ನು ಗುರುತಿಸಿ.
Describe the uses of herbs in nutraceuticals and cosmeceuticals.
ನ್ಯೂಟ್ರಾಸಿಯುಟಿಕಲ್ಸ್ ಮತ್ತು ಕಾಸ್ಮೆಸಿಯುಟಿಕಲ್ ಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಗಿಡಮೂಲಿಕೆಗಳ ಉಪಯೋಗಗಳನ್ನು ವಿವರಿಸಿ.
Discuss the principles of alternative system of medicines.
ಪರ್ಯಾಯ ಔಷಧ ಪದ್ಧತಿಯ ತತ್ವಗಳನ್ನು ಚರ್ಚಿಸಿ.
Describe the importance of quality control of drugs of natural origin.
ನೈಸರ್ಗಿಕ ಮೂಲದ ಔಷಧಗಳ ಗುಣಮಟ್ಟ ನಿಯಂತ್ರಣದ ಪ್ರಾಮುಖ್ಯತೆಯನ್ನು ವಿವರಿಸಿ.
Chapter Topic Hours
CHAPTER-1. Definition, history, present status and scope of Pharmacognosy 2Hrs
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ-1. ಫಾರ್ಮಾಕಾಗ್ನೋಸಿಯ ವ್ಯಾಖ್ಯಾನ, ಇತಿಹಾಸ, ಪ್ರಸ್ತುತ ಸ್ಥಿತಿ ಮತ್ತು ವ್ಯಾಪ್ತಿ 2 ಗಂಟೆಗಳು
CHAPTER-2 Classification of drugs: ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ-2 ಔಷಧಗಳ ವರ್ಗೀಕರಣ:
Alphabetical
Taxonomical
Morphological
Pharmacological
Chemical
Chemo-taxonomical 4Hrs
ಅಕಾರಾದಿ
ಟ್ಯಾಕ್ಸೊನೋಮಿಕಲ್
ರೂಪಶಾಸ್ತ್ರ
ಫಾರ್ಮಕಾಲಜಿಕಲ್
ರಾಸಾಯನಿಕ
ಕೀಮೋ-ಟ್ಯಾಕ್ಸೊನೋಮಿಕಲ್
CHAPTER-3. Quality control of crude drugs: o Different methods of adulteration of crude drugs o Evaluation of crude drugs. 6Hrs.
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ-3. ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಗಳ ಗುಣಮಟ್ಟ ನಿಯಂತ್ರಣ: ಓ ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಗಳ ಕಲಬೆರಕೆಯ ವಿಭಿನ್ನ ವಿಧಾನಗಳು ಓ ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಗಳ ಮೌಲ್ಯಮಾಪನ. 6 ಗಂಟೆಗಳು.
CHAPTER-4. Brief outline of occurrence, distribution, isolation, identification tests, therapeutic activity and pharmaceutical applications of alkaloids, terpenoids, glycosides, volatile oils, tannins and resins. 6Hrs.
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ-4. ಸಂಭವಿಸುವಿಕೆ, ವಿತರಣೆ, ಪ್ರತ್ಯೇಕತೆ, ಗುರುತಿಸುವಿಕೆ ಪರೀಕ್ಷೆಗಳು, ಚಿಕಿತ್ಸಕ ಚಟುವಟಿಕೆ ಮತ್ತು ಆಲ್ಕಲಾಯ್ಡ್ ಗಳು, ಟೆರ್ಪೆನಾಯ್ಡ್ ಗಳು, ಗ್ಲೈಕೋಸೈಡ್ ಗಳು, ಬಾಷ್ಪಶೀಲ ತೈಲಗಳು, ಟ್ಯಾನಿನ್ ಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ರಸಿನ್ ಗಳ ಔಷಧೀಯ ಅನ್ವಯಗಳ ಸಂಕ್ಷಿಪ್ತ ರೂಪರೇಖೆ. 6 ಗಂಟೆಗಳು.
CHAPTER-5. Biological source, chemical constituents and therapeutic efficacy of the following categories of crude drugs. 30Hrs.
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ-5. ಜೈವಿಕ ಮೂಲ, ರಾಸಾಯನಿಕ ಘಟಕಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಗಳ ಈ ಕೆಳಗಿನ ವರ್ಗಗಳ ಚಿಕಿತ್ಸಕ ಪರಿಣಾಮಕಾರಿತ್ವ.
Laxatives: Aloe, Castor oil, ispaghula, Senna
Cardiotonic: Digitalis, Arjuna
Carminatives and G.l. regulators: Coriander, Fennel, Cardamom, Ginger, Clove, Black Pepper, Asafoetida, Nutmeg, Cinnamon.
Astringents: Myrobalan, Black Catechu, Pale Catechu
Drugs acting on nervous system: Hyoscyamus, Belladonna, Ephedra, Opium, Tea leaves,
Coffee seeds, Coca.
Anti-hypertensive: Rauwolfia
Antitussive: Vasaka, Tolu Balsam
Anti-rheumatics: Colchicum seed
ವಿರೇಚಕಗಳು: ಅಲೋ, ಹರಳೆಣ್ಣೆ, ಇಸ್ಪಘುಲಾ, ಸೆನ್ನಾ
ಕಾರ್ಡಿಯೋಟೋನಿಕ್: ಡಿಜಿಟಲಿಸ್, ಅರ್ಜುನ
ಕಾರ್ಮಿನೇಟಿವ್ಸ್ ಮತ್ತು ಜಿ.ಎಲ್. ನಿಯಂತ್ರಕರು: ಕೊತ್ತಂಬರಿ, ಸೋಂಪು, ಏಲಕ್ಕಿ, ಶುಂಠಿ, ಲವಂಗ, ಕರಿಮೆಣಸು, ಅಸಾಫೋಟಿಡಾ, ಜಾಯಿಕಾಯಿ, ದಾಲ್ಚಿನ್ನಿ.
ಆಸ್ಟ್ರಿಂಜೆಂಟ್ಸ್: ಮೈರೋಬಾಲನ್, ಬ್ಲ್ಯಾಕ್ ಕ್ಯಾಟೆಚು, ಪೇಲ್ ಕ್ಯಾಟೆಚು
ನರವ್ಯೂಹದ ಮೇಲೆ ಕಾರ್ಯನಿರ್ವಹಿಸುವ ಔಷಧಿಗಳು: ಹ್ಯೋಸ್ಸಿಯಮಸ್, ಬೆಲ್ಲಡೊನ್ನಾ, ಎಫೆಡ್ರಾ, ಅಫೀಮು, ಚಹಾ ಎಲೆಗಳು,
ಕಾಫಿ ಬೀಜಗಳು, ಕೋಕಾ.
ಅಧಿಕ ರಕ್ತದೊತ್ತಡ ವಿರೋಧಿ: ರೌವೂಲ್ಫಿಯಾ
ಆಂಟಿಟುಸ್ಸಿವ್: ವಾಸಕ, ಟೋಲು ಬಾಲ್ಸಮ್
ಆಂಟಿ-ರುಮ್ಯಾಟಿಕ್ಸ್: ಕೋಲ್ಚಿಕಮ್ ಬೀಜ
Anti-tumour: Vinca, Podophyllum
Antidiabetics: Pterocarpus, Gymnema
Diuretics: Gokhru, Punarnava
Antidysenteric ipecacuanha
Antiseptics and disinfectants: Benzoin, Myrrh, Neem, Turmeric
Antimalarials: Cinchona, Artemisia
Oxytocic: Ergot
Vitamins: Cod liver oil, Shark liver oil
Enzymes: Papaya, Diastase, Pancreatin, Yeast
Pharmaceutical Aids: Kaolin, Lanolin, Beeswax, Acacia, Tragacanth, Sodium alginate, Agar,
Guar gum, Gelatine.
Miscellaneous Squill, Galls, Ashwagandha, Tulsi, Guggul.
ಆಂಟಿ-ಟ್ಯೂಮರ್: ವಿಂಕಾ, ಪೊಡೊಫಿಲ್ಲಮ್
ಆಂಟಿಡಯಾಬಿಟೀಕ್ಸ್: ಟೆರೊಕಾರ್ಪಸ್, ಜಿಮ್ನೆಮಾ
ಮೂತ್ರವರ್ಧಕಗಳು: ಗೋಖ್ರು, ಪುನಾರ್ನಾವ
ಅವ್ಯವಸ್ಥಿತ ಸೆಂಟೆರಿಕ್ ಇಪೆಕಾಕುವಾನ್ಹಾ
ಆಂಟಿಸೆಪ್ಟಿಕ್ ಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಸೋಂಕುನಿವಾರಕಗಳು: ಬೆಂಜೋಯಿನ್, ಮಿರ್ಹ್, ಬೇವು, ಅರಿಶಿನ
ಮಲೇರಿಯಾ ನಿರೋಧಕಗಳು: ಸಿಂಕೋನಾ, ಆರ್ಟೆಮಿಸಿಯಾ
ಆಕ್ಸಿಟೋಸಿಕ್: ಎರ್ಗಾಟ್
ವಿಟಮಿನ್ ಗಳು: ಕಾಡ್ ಲಿವರ್ ಆಯಿಲ್, ಶಾರ್ಕ್ ಲಿವರ್ ಆಯಿಲ್
ಕಿಣ್ವಗಳು: ಪಪ್ಪಾಯಿ, ಡಯಾಸ್ಟೇಸ್, ಪ್ಯಾಂಕ್ರಿಯಾಟಿನ್, ಯೀಸ್ಟ್
ಔಷಧೀಯ ಏಡ್ಸ್: ಕಾವೊಲಿನ್, ಲನೋಲಿನ್, ಬೀಸ್ ವ್ಯಾಕ್ಸ್, ಅಕೇಶಿಯಾ, ಟ್ರಾಗಕ್ಯಾಂತ್, ಸೋಡಿಯಂ ಆಲ್ಜಿನೇಟ್, ಅಗರ್,
ಗುರ್ ಗಮ್, ಜಿಲೆಟಿನ್.
ಇತರೆ ಸ್ಕ್ವಿಲ್, ಗಾಲ್ಸ್, ಅಶ್ವಗಂಧ, ತುಳಸಿ, ಗುಗ್ಗುಲ್.
CHAPTER-6. Plant fibres used as surgical dressings: Cotton, silk, wool and regenerated fibres. Sutures - Surgical Catgut and Ligatures. 3Hrs.
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ-6. ಶಸ್ತ್ರಚಿಕಿತ್ಸೆಯ ಡ್ರೆಸ್ಸಿಂಗ್ ಗಳಾಗಿ ಬಳಸುವ ಸಸ್ಯ ನಾರುಗಳು: ಹತ್ತಿ, ರೇಷ್ಮೆ, ಉಣ್ಣೆ ಮತ್ತು ಪುನರುತ್ಪಾದಿತ ನಾರುಗಳು. ಸೂಚರ್ ಗಳು - ಸರ್ಜಿಕಲ್ ಕ್ಯಾಟ್ಗಟ್ ಮತ್ತು ಲಿಗೇಚರ್ಗಳು. 3 ಗಂಟೆಗಳು.
CHAPTER-7. Basic principles involved in the traditional systems of medicine like: Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani and Homoeopathy o Method of preparation of Ayurvedic formulations like: Arista, Asava, Gutika, Taila, Churna, Lehya and Bhasma 8Hrs.
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ-7. ಸಾಂಪ್ರದಾಯಿಕ ವೈದ್ಯಕೀಯ ಪದ್ಧತಿಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಒಳಗೊಂಡಿರುವ ಮೂಲ ತತ್ವಗಳು: ಆಯುರ್ವೇದ, ಸಿದ್ಧ, ಯುನಾನಿ ಮತ್ತು ಹೋಮಿಯೋಪತಿ ಓ ಆಯುರ್ವೇದ ಸೂತ್ರೀಕರಣಗಳ ತಯಾರಿಕೆಯ ವಿಧಾನ: ಅರಿಸ್ಟಾ, ಅಸಾವ, ಗುಟಿಕಾ, ಟೈಲಾ, ಚೂರ್ನಾ, ಲೆಹ್ಯಾ ಮತ್ತು ಭಾಸ್ಮಾ 8 ಗಂಟೆಗಳು.
CHAPTER-8. Role of medicinal and aromatic plants in national economy and their export potential 2Hrs.
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ-8. ರಾಷ್ಟ್ರೀಯ ಆರ್ಥಿಕತೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಔಷಧೀಯ ಮತ್ತು ಸುವಾಸನೆಯುಕ್ತ ಸಸ್ಯಗಳ ಪಾತ್ರ ಮತ್ತು ಅವುಗಳ ರಫ್ತು ಸಾಮರ್ಥ್ಯ 2 ಗಂಟೆಗಳು.
CHAPTER-9. Herbs as health food: Brief introduction and therapeutic applications of:
Nutraceuticals, Antioxidants, Probiotics, Probiotics, Dietary fibres, Omega-3-fatty acids, Spirulina, Carotenoids, Soya and Garlic. 4Hrs.
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ-9. ಆರೋಗ್ಯ ಆಹಾರವಾಗಿ ಗಿಡಮೂಲಿಕೆಗಳು: ಸಂಕ್ಷಿಪ್ತ ಪರಿಚಯ ಮತ್ತು ಚಿಕಿತ್ಸಕ ಅನ್ವಯಗಳು:
ನ್ಯೂಟ್ರಾಸಿಯುಟಿಕಲ್ಸ್, ಆಂಟಿಆಕ್ಸಿಡೆಂಟ್ ಗಳು, ಪ್ರೋಬಯಾಟಿಕ್ಸ್, ಪ್ರೋಬಯಾಟಿಕ್ಸ್, ಡಯಟರಿ ಫೈಬರ್ ಗಳು, ಒಮೆಗಾ-3-ಕೊಬ್ಬಿನಾಮ್ಲಗಳು, ಸ್ಪಿರುಲಿನಾ, ಕ್ಯಾರೊಟಿನಾಯ್ಡ್ ಗಳು, ಸೋಯಾ ಮತ್ತು ಬೆಳ್ಳುಳ್ಳಿ. 4 ಗಂಟೆಗಳು.
CHAPTER-10. Introduction to herbal formulations 4Hrs.
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ-10. ಗಿಡಮೂಲಿಕೆ ಸೂತ್ರೀಕರಣಗಳ ಪರಿಚಯ 4 ಗಂಟೆಗಳು.
CHAPTER-11. Herbal cosmetics: Sources, chemical constituents, commercial preparations,
therapeutic and cosmetic uses of: Aloe vera gel, Almond oil, Lavender oil, Olive oil, Rosemary oil, SandalWood oil. 4Hrs.
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ-11. ಗಿಡಮೂಲಿಕೆ ಸೌಂದರ್ಯವರ್ಧಕಗಳು: ಮೂಲಗಳು, ರಾಸಾಯನಿಕ ಘಟಕಗಳು, ವಾಣಿಜ್ಯ ಸಿದ್ಧತೆಗಳು,
ಚಿಕಿತ್ಸಕ ಮತ್ತು ಸೌಂದರ್ಯವರ್ಧಕ ಉಪಯೋಗಗಳು: ಅಲೋವೆರಾ ಜೆಲ್, ಬಾದಾಮಿ ಎಣ್ಣೆ, ಲ್ಯಾವೆಂಡರ್ ಎಣ್ಣೆ, ಆಲಿವ್ ಎಣ್ಣೆ, ರೋಸ್ಮೇರಿ ಎಣ್ಣೆ, ಸ್ಯಾಂಡಲ್ ವುಡ್ ಎಣ್ಣೆ. 4 ಗಂಟೆಗಳು.
CHAPTER-12. Phytochemical investigation of drugs 2Hrs.
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ-12. ಔಷಧಗಳ ಫೈಟೋಕೆಮಿಕಲ್ ತನಿಖೆ 2ಗಂಟೆ.
PHARMACOGNOSY - PRACTICAL
Course Code: ER20-13P
75 Hours (3 Hours/week)
Scope: This course is designed to train the students in physical identification, morphological characterization, physical and chemical characterization, and evaluation of commonly used herbal drugs. Course Objectives: This course will provide hands-on experiences to the students in
ವ್ಯಾಪ್ತಿ: ಈ ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ಅನ್ನು ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಗಳಿಗೆ ಭೌತಿಕ ಗುರುತಿಸುವಿಕೆ, ರೂಪಶಾಸ್ತ್ರೀಯ ಗುಣಲಕ್ಷಣ, ಭೌತಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ರಾಸಾಯನಿಕ ಗುಣಲಕ್ಷಣ ಮತ್ತು ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯವಾಗಿ ಬಳಸುವ ಗಿಡಮೂಲಿಕೆ ಔಷಧಿಗಳ ಮೌಲ್ಯಮಾಪನದಲ್ಲಿ ತರಬೇತಿ ನೀಡಲು ವಿನ್ಯಾಸಗೊಳಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ. ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ಉದ್ದೇಶಗಳು: ಈ ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಗಳಿಗೆ ಹ್ಯಾಂಡ್-ಆನ್ ಅನುಭವಗಳನ್ನು ಒದಗಿಸುತ್ತದೆ
1. identification of the crude drugs based on their morphological characteristics
1. ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಗಳ ರೂಪಶಾಸ್ತ್ರೀಯ ಗುಣಲಕ್ಷಣಗಳ ಆಧಾರದ ಮೇಲೆ ಗುರುತಿಸುವುದು
2. Various characteristic anatomical characteristics of the herbal drugs studied
through the transverse section.
2. ಅಧ್ಯಯನ ಮಾಡಿದ ಗಿಡಮೂಲಿಕೆ ಔಷಧಗಳ ವಿವಿಧ ವಿಶಿಷ್ಟ ಅಂಗರಚನಾ ಗುಣಲಕ್ಷಣಗಳು
ಟ್ರಾನ್ಸ್ ವರ್ಸ್ ವಿಭಾಗದ ಮೂಲಕ.
3. Physical and chemical tests to evaluate the crude drugs Course Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, the students will be able to
3. ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಗಳ ಮೌಲ್ಯಮಾಪನಕ್ಕಾಗಿ ಭೌತಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ರಾಸಾಯನಿಕ ಪರೀಕ್ಷೆಗಳು ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ಫಲಿತಾಂಶಗಳು: ಈ ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ಯಶಸ್ವಿಯಾಗಿ ಪೂರ್ಣಗೊಂಡ ನಂತರ, ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಗಳು ಮಾಡಲು ಸಾಧ್ಯವಾಗುತ್ತದೆ
Identify the given crude drugs based on the morphological characteristics.
ರೂಪಶಾಸ್ತ್ರೀಯ ಗುಣಲಕ್ಷಣಗಳ ಆಧಾರದ ಮೇಲೆ ನೀಡಲಾದ ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಗಳನ್ನು ಗುರುತಿಸಿ.
Take a transverse section of the given crude drugs.
ನೀಡಲಾದ ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಿಗಳ ಅಡ್ಡಭಾಗವನ್ನು ತೆಗೆದುಕೊಳ್ಳಿ.
Describe the anatomical characteristics of the crude drug under
microscopical conditions.
ಅಡಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧದ ಅಂಗರಚನಾ ಗುಣಲಕ್ಷಣಗಳನ್ನು ವಿವರಿಸಿ
ಸೂಕ್ಷ್ಮಾತಿಸೂಕ್ಷ್ಮ ಪರಿಸ್ಥಿತಿಗಳು.
Carry out the physical and chemical tests to evaluate the given crude drugs.
ನೀಡಲಾದ ಕಚ್ಚಾ ಔಷಧಿಗಳನ್ನು ಮೌಲ್ಯಮಾಪನ ಮಾಡಲು ಭೌತಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ರಾಸಾಯನಿಕ ಪರೀಕ್ಷೆಗಳನ್ನು ಮಾಡಿ.
Morphological identification of the following drugs: ispaghula, Senna, Coriander, Fennel, Cardamom, Ginger, Nutmeg, Black Pepper, Cinnamon, Clove, Ephedra, Rauwolfia, Gokhru, Punarnava, Cinchona, Agar.
ಈ ಕೆಳಗಿನ ಔಷಧಗಳ ರೂಪಶಾಸ್ತ್ರೀಯ ಗುರುತಿಸುವಿಕೆ: ಇಸ್ಪಾಘುಲಾ, ಸೆನ್ನಾ, ಕೊತ್ತಂಬರಿ, ಸೋಂಪು, ಏಲಕ್ಕಿ, ಶುಂಠಿ, ಜಾಯಿಕಾಯಿ, ಕರಿಮೆಣಸು, ದಾಲ್ಚಿನ್ನಿ, ಲವಂಗ, ಎಫೆದ್ರಾ, ರೌವೂಲ್ಫಿಯಾ, ಗೋಖ್ರು, ಪುನಾರ್ನವ, ಚಿಂಚೋನಾ, ಅಗರ್.
Gross anatomical studies (Transverse Section) of the following drugs: Ajwain, Datura, Cinnamon, Cinchona, Coriander, Ashwagandha, Liquorice, Clove, Curcuma, Nux-vomica, Vasaka
ಈ ಕೆಳಗಿನ ಔಷಧಗಳ ಒಟ್ಟು ಅಂಗರಚನಾ ಅಧ್ಯಯನಗಳು (ಟ್ರಾನ್ಸ್ ವರ್ಸ್ ವಿಭಾಗ) : ಅಜ್ವೈನ್, ದತುರಾ, ದಾಲ್ಚಿನ್ನಿ, ಸಿಂಕೋನಾ, ಕೊತ್ತಂಬರಿ, ಅಶ್ವಗಂಧ, ಮದ್ಯ, ಲವಂಗ, ಕುರ್ಕುಮಾ, ನಕ್ಸ್-ವೊಮಿಕಾ, ವಾಸಕ
Physical and chemical tests for evaluation of any FIVE of the following drugs:
ಈ ಕೆಳಗಿನ ಐದು ಔಷಧಗಳ ಮೌಲ್ಯಮಾಪನಕ್ಕಾಗಿ ದೈಹಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ರಾಸಾಯನಿಕ ಪರೀಕ್ಷೆಗಳು:
Asafoetida,
Benzoin,
Pale catechu,
Black catechu,
Castor oil,
Acacia,
Tragacanth,
Agar,
Guar gum,
Gelatine.
ಅಸಾಫೋಟಿಡಾ,
ಬೆಂಜೋಯಿನ್,
ಪೇಲ್ ಕ್ಯಾಟೆಚು,
ಕಪ್ಪು ಕ್ಯಾಟೆಚು,
ಹರಳೆಣ್ಣೆ,
ಅಕೇಶಿಯಾ,
ಟ್ರಾಗಕ್ಯಾಂತ್,
ಅಗರ್,
ಗುರ್ ಗಮ್,
ಜಿಲೆಟಿನ್ .
Assignments: The students shall be asked to submit the written assignments on the following topics (One assignment per student per sessional period. i.e., a minimum of THREE assignments per student)
ನಿಯೋಜನೆಗಳು: ಈ ಕೆಳಗಿನ ವಿಷಯಗಳ ಮೇಲೆ ಲಿಖಿತ ಅಸೈನ್ ಮೆಂಟ್ ಗಳನ್ನು ಸಲ್ಲಿಸುವಂತೆ ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಗಳನ್ನು ಕೇಳಬೇಕು (ಪ್ರತಿ ಸೆಷನ್ ಅವಧಿಗೆ ಪ್ರತಿ ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಗೆ ಒಂದು ಅಸೈನ್ ಮೆಂಟ್. ಅಂದರೆ ಪ್ರತಿ ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಗೆ ಕನಿಷ್ಠ ಮೂರು ಅಸೈನ್ ಮೆಂಟ್ ಗಳು)
1. Market preparations of various dosage forms of Ayurvedic, Unani, Siddha, Homoeopathic (Classical and Proprietary), indications, and their labelling requirements.
1. ಆಯುರ್ವೇದ, ಯುನಾನಿ, ಸಿದ್ಧ, ಹೋಮಿಯೋಪತಿಕ್ (ಶಾಸ್ತ್ರೀಯ ಮತ್ತು ಸ್ವಾಮ್ಯದ) ವಿವಿಧ ಡೋಸೇಜ್ ರೂಪಗಳ ಮಾರುಕಟ್ಟೆ ಸಿದ್ಧತೆಗಳು, ಸೂಚನೆಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಅವುಗಳ ಲೇಬಲಿಂಗ್ ಅವಶ್ಯಕತೆಗಳು.
2. Market preparations of various herbal formulations and herbal cosmetics, indications, and their labelling requirements.
2. ವಿವಿಧ ಗಿಡಮೂಲಿಕೆ ಗಳ ಸೂತ್ರೀಕರಣಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಗಿಡಮೂಲಿಕೆ ಸೌಂದರ್ಯವರ್ಧಕಗಳ ಮಾರುಕಟ್ಟೆ ಸಿದ್ಧತೆಗಳು, ಸೂಚನೆಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಅವುಗಳ ಲೇಬಲಿಂಗ್ ಅವಶ್ಯಕತೆಗಳು.
3. Herb-Drug interactions documented in the literature and their clinical significance.
3. ಸಾಹಿತ್ಯದಲ್ಲಿ ದಾಖಲಿಸಲಾದ ಗಿಡಮೂಲಿಕೆ-ಔಷಧ ಸಂವಹನಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಅವುಗಳ ವೈದ್ಯಕೀಯ ಮಹತ್ವ.
Field Visit: The students shall be taken in groups to a medicinal garden to witness and understand the nature of various medicinal plants discussed in theory and practical courses. Additionally, they shall be taken in groups to the pharmacies of traditional systems of medicines to understand the availability of various dosage forms and their labelling requirements. individual reports from each student on their learning experience from the field visit shall be submitted.
ಕ್ಷೇತ್ರ ಭೇಟಿ: ಸಿದ್ಧಾಂತ ಮತ್ತು ಪ್ರಾಯೋಗಿಕ ಕೋರ್ಸ್ ಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಚರ್ಚಿಸಲಾದ ವಿವಿಧ ಔಷಧೀಯ ಸಸ್ಯಗಳ ಸ್ವರೂಪವನ್ನು ವೀಕ್ಷಿಸಲು ಮತ್ತು ಅರ್ಥಮಾಡಿಕೊಳ್ಳಲು ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಗಳನ್ನು ಗುಂಪುಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಔಷಧೀಯ ತೋಟಕ್ಕೆ ಕರೆದೊಯ್ಯಬೇಕು. ಹೆಚ್ಚುವರಿಯಾಗಿ, ವಿವಿಧ ಡೋಸೇಜ್ ನಮೂನೆಗಳ ಲಭ್ಯತೆ ಮತ್ತು ಅವುಗಳ ಲೇಬಲಿಂಗ್ ಅವಶ್ಯಕತೆಗಳನ್ನು ಅರ್ಥಮಾಡಿಕೊಳ್ಳಲು ಅವುಗಳನ್ನು ಸಾಂಪ್ರದಾಯಿಕ ಔಷಧಪದ್ಧತಿಗಳ ಔಷಧಾಲಯಗಳಿಗೆ ಗುಂಪುಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಕರೆದೊಯ್ಯಲಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಕ್ಷೇತ್ರ ಭೇಟಿಯಿಂದ ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬ ವಿದ್ಯಾರ್ಥಿಯ ಕಲಿಕೆಯ ಅನುಭವದ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ವೈಯಕ್ತಿಕ ವರದಿಗಳನ್ನು ಸಲ್ಲಿಸಬೇಕು.
D3300596/1/MAY 1996
Government Of Karnataka
BOARD OB EXAMINING AUTHORITY
DIPLMA IN PHARMACY (ER91)
First Year D.Pharm Examinations, May 1996
Time 3 hours] PHARMACOGNOSY (ER91). [Max.Marks 8O
Note: Answer any ten Questions from SECTION A and any Three Questions
From SECTION B including Question No.14 which is Compulsory.
SECTION-A 4x10=40
1. define crude drug. How do you classify crude drugs?
2. Describe macroscopic characters of cinnamon and Senna.
3. Give name, official source, family and uses of one drug each
Belonging to the following families
(a) Rubiaceae (b) Solanaceae (c) Apocyanaceae (d) Umbelliferae
4. Give difference between Black and pale catechu.
5. What are saponin glycosides? Write Botanical source, family, Active constituents and uses of glycyrrhiza.
6. Give one example for drug used as following. Give their Source, official source and their active constituents. Laxative (b) Insecticide (c) antimalarial (d) antidysentirics.
7. Name a drug used as cardio tonic. Write identification tests for same.
8. Write differences between fixed oils and fats. Give two e.g. each,
9. Give one e.g. for a dried juice and latex cc, uses and family.
10. Write chemical constituent and uses of
(a) Ispaghula (b) Neem (c) Ephedra (d) Rhubarb
11. Write a note on solanaceous alkaloids.
12. What are balsamic resins? How to distinguish Sumatra and Sian Benzoin,
13. Describe method of preparation of Absorbent cotton Give its Botanical source, famlly, uses and constituent.
SECTION-B (40
14. (a)Describe Life cycle of Ergot
(b)Write a note on cultivation and collection. Give its constituents and uses. 6+5+3
OR
Define evaluation of a drug and write a note on microscopic evaluation 4+10
15. Define alkaloids. Give their important properties and tests for their identification.
Classify alkaloids with examples. 2+3+4+4
16 (a) Describe anatomy of clove, with & neat labelled diagram
(b) Explain method of cultivation and collection of opium and Senna 6+7
17 (a) write a note on natural drugs antidiabetics and antimalarials.
(b) Give tests for the identification of (a) Agar (b) Gelatine 7+6
D3300397/2/MAR 1997
Government Of Karnataka
BOARD OB EXAMINING AUTHORITY
DIPLMA IN PHARMACY (ER91)
First Year D.Pharm Examinations, March 1997
Time 3 hours] PHARMACOGNOSY (ER91). [Max.Marks 8O
Note: Answer any ten Questions from SECTION A and any Three Questions
From SECTION B including Question No.14 which is Compulsory.
SECTION-A 4x10=40
1.Write Briefly on Indian System of Medicine
2.Give Name, source and Uses of One drug belonging families
Anthracene, Loganiaceae, Euphorbiaceae, Myrataceae
3. tion four Carminative with Source and family
4, Name two Antirheumatic drugs with Source, Family &, Constituents.
5.Write a note on enzymes, Explain the collection of Papain
6.Write source, biological features of clove with a neat dliagram
7.Give example each for Oleoresin and Balsam resin. Mention Source and, Uses
8. Give one specific test each for identification of Cardiac and Anthraquinone glycosides & Discuss tests.
9. Mention Name, source, family and Uses of Crude drugs contain following constituents Ferulic acid, Bassorin, Invert Sugar, Oannabinol
10 Name the Source, Active Constituents and uses of
Neem, fobdooo, Black Pepper, Linseed,
1l Describe morphological feature of Umbelliferous fruit
12 Give One Otr"io", identifioation tcst for Eoney lgrrn Cinnanon, Benzoin.
18 Defius (a) Altatoidr a, ud (6) Lipiar
EffiEION_B . 40
tq Briefly digouss difrerent methode of olacsifioetion of orude d, rugs. 7 +7
Erplein the olmsiflcation. OB
(o) Wrih a robc ou oolleotion aa.rl.pleparetiou of lonrra.
(D) With lebelleil iliogran Erplain enrtody of sen3e. 6+8.
t5 Deflne tanninr, olassify them $ith Examples. Give theil inportant
propertiee anil tests for itlsntifioation. 2+4+3+l
1.6 Mention auy ooe oruds drug belonging to tho family solrnaoer, q.
Give its Botanical Source, Family, Active constituent.
With labelloid diagram description its morphological features s+s+?
17 Write, st6 Butdrcg and Ligature 1flcntion the difiorcnc0s, [61es61
Ihsorba, b.te snd no[obsorbable Buturor with oxonplol.
Elplau ahiaulial method of gt€rfilization of oatgui. t++, &
D3301097/3/OCT 1997
D3301097 Govsmnent oI Karnataka
ROAND OF DXAMININO AUTTIOBITY
DIPt0DTA IN PHARMACY (EBteol)
D. Pharm PtrtI Eramiuatiour 0ctober 1997
flme B lloursl PEARIIAC0GN0SI [Mar. Merke 80
lVotc 3.Answel eqy ?EN _questions from $ection A snd ty IH&DE questions
from $eotibn B. Iuclutling questiou No. t4 whioh is compul"ory.l
4 x l0=40
1 Define Pharmacognosy. Name various systems of classification of crude drug.
2 Write the ofrcirl rcuroe, fmily, ocndituenta rnil useg of urilemon anil Nutmeg.
3 Give the ootivo cotrltitucntr rnd ures of
(a) Ilyooo srnuE (D) Arjuna (c) Senuo (d Lanolir
4 Write the morphologioel charrcters of (i) Ipecrcuanho (D) Nurvomica
6 How do yoti, AiedqEtirct sotton fibre fronr rool fibres?
6 Give souroG, urer of drug coutaining followjgg oouotitffitr.
(d Dphoilrine (0) Py, rethrin (o) 0atochin (d) Diosgenin
T [Mlrat aro guEE 1 E"o.u ds ysu ili#fngut$h.Asaoia from tregaoanth ?
I Gllve 1 eS ffiiilE, ry [rrftrg fuIffiB, 6t[on, vrite their so^Etsoa aad ooi
(i) O4ytooio (ii1 Auticoncer (iii) Antiseptio (iv) Antispasmodic
9 Nerne ihugs onteining inilole alhaloiils, c6o, Esgiit[ehts user of a11y otwof them.
10 l) eeoril.ro Bethod of pr.eparation of opiun
1l Write spooifio identiffoation tort for Asefoetiala.
Write princtple innolved ia oombhed umbellifo, none tost.
12 Name 2 itrrugs oontaining orrtliao gtyoCIiiles teats for card, iao glyoooidee,
18 Wbat are teunins I Classify them with eramples
SEflEIONB v,40
14 Writc atroteotr hhtory & toopo gfPhlrmloognoty.
OR
What is evdutiso of onlde drugs.
lYrite o roto on Physioal & ohemiosl evrlurtion. lr
15 (o) T[hot are enthrocene glycosider ?
(D) Give the Botaniool souroe fanily, comtituents & u$r of llors,
(o) lfrite tho nothod of prepbration of Aloe. 8+l+0
16 lrito notos ou the folloving.
(o) Suturm ond ligrturer, (D1 Cultivation & oolloctlgn 0f rennr 6+f,
17 (o) Desuibo rnotony of oinnemo[ 0f tiudom dfi hbclted ilirprm.
(b) I[rlte 0 r0t0 oD umrolliferous falih.
E
D3300999/4/SEP 1999
D8800999 Government of Karnataka
BOARD OX EXAMINING AUTHORITY
DIPLOMA IN PHARMACY (ER91)
DPharm PartI Examinations September 1999
Time 3 Hours PHARMACOGNOSY (AA gl )
[Max. Markg 80
[Ifoac(l) Answer Any ten questions from section and any IHhDE queetions
from Section B. Including question No. t4 which is compulsory.
X10
1 G$ive oo.rrer sorlBcrgi f, o, mll y uses of drugof faailies. (") Apoeyauaooao (ftI Usheose (o) Oleaoeae (d) Solanroeoe
2 Glive one oLeaiocl tcpt fory, [.iilegttfioatioa of followiag. (c) .&srfioatfldb P] Hnus5r (a] Bffnolllage (dl Oardenolides
3 Compare f, olloritrg
(a) Gtums aud, muollagos (e) Boilable ard NoaBoilable Oatgut
(D) Glyoot eari AglJroon (d) Tcqg Al.Hoids snd PsuedoAlkaloids
5 Morpholoefy ith diagrem (a) IpeoapFpaha (6) Nux vomica
6 .Desoribe tests for identifioation of silk fibres
6 ssurse and usos of (a) TobEooo (D) Aiowan (o) Diastase (d) Pte roosrpug
7 Deecribe pharmeoologioal and ohqpipl olEi$oa0ion of crdo
drugs with eonplcs. Msntion thoir adluruffiwand dieadioutages.
8 lVrite a aote oa Adulterction of Orude Dmgp rith eooples.
I Give nouroc and uEoB of otude dmg whioh ooutain following coustituentr
(o) Bassorin (6) Serrulio aoid (o) Vitamia A (d) Codeine
10 Defiae Resins. Give their properties and olassifieation with eramples.
t1 Name two antidiabetios, their soutco and importnnt coastituents.
12 Dc6ne (o) Crude l) rugs (D) Organised orude drugs
(o) FharnooogDosy (d) Unorgodissd orudo drugs
tg Give aouro6s, ooactituents, usc1 ond tmto for Glelotin and Myrrh
sE0EloNtB (
(I0 Err&s
14 Desotib€ oollostfio.s, plamffidon, storgen oonstituents and nses
of Ergot arrd, Digttorltl. OB ?+?
Definc EvaluatioD.lVrite a nots on biologioal evaluation and
Phlsical Evaluation. 2+6+0
16 (d Describe ths souroe, preparation usss nd offlcial tesbs for
gsjgioalOotton woot ?
(A) What are regenerated fibres ? &kplain with examples. 9+
16 f) efine alkaloids aud olassifythem. with oxgrmpl6. Desstibe how
. atkaloide nriybe isolated from a, orude drug. 2 6+0
tT @l Givs mioroscopio oharecters of Nux Vomioa with diagram.
(0) lfLot in f. oreign laorganio Mattm and.Stomatal Nlmber ?
IVrite about, tbeir inrPortaDoe. 2+6+6
D3300603/5/JUN 2003
Government of Karnataka
BOARD OF EXAI4INING AUTHORTTY
D.Pharm PartI Eramination (ER91)
Time3Hours PHARMACOGNOSY
[max. marks80
[Note Answer any TEN questions from Section A and any THREE questions
from Section B including question No.14 which is compulsory
SECTIONA
Discuss briefly llistory of PharmacogBosy.
Give botanical sourice and use of dmgs containing following.
constittrents. a) Vincristine b) EmAiie c) Ferrulic acid d) Atropine
Describe morphological characters of a) Vasaka b) Clove
Exptain following tEsts. a) Combined umbelliferone test b) FicF63 tEst
Write a note_on gums and muclllages.
Name botan[al iourc", cherniial constituents and uses of a) Amla b) Aloes
Give name and uses of any one drug helonging to the following families
a) Zingiberaceae b) .r.auraceae c) Leguminosae d) Euphorbiaceae
Define a) Suture b) Stomatal index c) Glycoside d) Diuretic
Write a briefnote on crude drug monograph.
Name the imporant chemical constituents and uses of the following
a) Senna b) Isapgol c) Pale catechu d) Honey
What are alkaloids? Classifu them with exanrpleS.
Give one example of a crude drug used as the following with their source
and active constituents. a) Colouring agent b) Inseoticide
c) Emulsifyng agent d) turti gout rr Write the source, preparation and uses of Cotton
SECTION.B V
Define evaluation. Name different methods of evaluation. Discuss
morphologtcal and microscopical evaluation with suiable examples urf, 14
What is adulteration? Write a brief note on different types of adulteration
With the help of a neat labeled diagram describe the microscopy of Fennel. Write a note on a) Tanrdns b) Opium,o
a) What are oardiac glycosides? Give source and active constituents of any two_dnrgs used as cardiotonics.
b) whst are resins? classi& them with suitable examples. r+6.
Write notes on a) Antiseptics and disinfectants b) Identification tests for alkaloids c) Natural fibres
D3300904/6/SEP 2004
D3 3ooe onfiBt$ffifffifitTfrlffi IrY
D.PHARM. PARTI EXAMINATION (ER91)
Time 3 Hours PHARMAC0GN0SY JMax. Marks.B0
N0fE Answer any TEN questions from SectionA and any THREE questions
From SectionB, including question No, 14 which is compulsory.
SECTION.A 4x1tr40
l. Define crude drug and technical product.
2. Describe morphological characters of Ispagula and Senna,
3. Define enzyme. Give source and uses of diastase and yeast.
4, Give official source and uses of drug containing following active principles
a) Filicic acid b) Anethole o) Emetine d) Arabin
5. Describe tests. a) Combined umbelliferone test b) modified Bornf4gger test.
6. Give name source and uses of any two crude drugs of Families.
a) Scrophularaceae b) Euphorbiaceae
7,Give cc and uses of a) Neem b) Nuxvomica c) Ephedra d) Podophyllum
8. Describe chemical classification of crude drugs with merits and demerits.
9. Write short notes on cardiac glycosides.
10, Name two crude drugs from animal source. Mention its source and uses
11. Define and classify tannins with suitable examples.
12. Name two crude drugs containing indole alkaloids and anthracene glycosides. Identification
Its source and uses.
13. Describe cultivation and collection of opium.
SECTIONB, 1ghrh
14. A) Describe life cycle of ergot,
b) Mention active principle and uses of ergot.
Q Explain drying processes for crude drugs 0R 6+4
a) Define drug evaluation and olassiS,
b) Explain chemical and biological evaluation, +10
15. a) Give morphology and microscopy of fennel with labelled diagram. 6+?
16. Give one confirmatory tests for a) Agar b) gelntin 0) tragacanth d) Benzoin [3
17. Write notes on a) Preparation of surgical catgut b) Adulteration practices
Surgical dressings’ r +Ss
D3300205/7/FEB 2005
D33OO2O5 GOVERNMENT OF IGRNATAKA
BOARD OF EXAIVIINING AUTIIORITY
D.PHARM, PART I EXAMINATIoNS (ER91)
Time, 3 Hoursl pntnUACOGNOSY [Max.Marls80
NorE Answer any TEN questions from SectionA and any THREE
questions from Section8 including question No, 14 which is compulsory.
SECTIONA 4x1o=40
l. Define Pharmacognosy and Crude drug,
2. Mention four carminatives wittr tlreir official source and family.
3. Write notes on Technical products,
4. Define Tannins and glycosido
5. Name two antirheumatic drug with official source and uses.
6. Name official source, active principles and uses of a) Tobacco b) Linseed
o) Nuxvomica d) Aconite
7. Dsfine volatile oils. CIassiS with examplos.,
8. Explain morphological classification with merits and dernerits,
9. Write notes on Siddha and Naturopathy.
I0. Mention name, souree and uses of each belonging to following families.
a) Acanthaceae b) Lauracea c) Apocyanaceae d) Burceraceae
11. Give official source and active principleand uses of crude drug containing
following active principles. a) Diosgenin b) Conessino c) Asafoetida rd) Emetine
12. Explain macrosgopic characters of Clove bud.
13. Name any two seed and bark dnrg with their main active principle and uses.
SECTION.B V
14 Explain Collection, preparation, storage conditions, active principles and uses of.
Opium and Digitalis OR 7+7
Give anatomical features with neat labeled diagrams of Datura and lpecac 7+7
l5 a) Define and olasifr alkaloids with example$, b) Explain isolation of alkaloids, 85
16 Give identifying tests for a) Acaoia b) Myrh o) Cardiac glycosidos
d) Anthraoene glycosides 3+3+3lA+316
17 Write notes on a) Physical evaluation b) Cyanogenetic glycosides 54+4
c) Drug conhining oxytooic
D3301005/8/OCT 2005
D3301005
GOVERNMEIT OF IGRNATA KA
BOARD OF EXAMINING AUTHORITY
D.PHARM. PART I EXAMINATIONS (ER91)
Pharmacognosy [Max. Marta_80
Time3 Hours
N0TEAnswer any TEN questions from SectionA and any THREE
Que$ions from SectionB including question No. 14 which is compulsory.
(Write diagrams wherever required)
SECTIONA 4Xt0
1. Explain morphological classification.
2. Write the botanical source, chemical constituents and uses of the drugs having oxytocic activity.
3. Write the botanical source and uses d) ragacanth.
4. Give the name and active constituents of any on9 q.ghlonging to the following category a) cardiotonic b) antileprotic c) antitussive d) flavouring agent.
5. Describe the morphological characters a) gokhru b) senna leaf
6. Name laxatives from plant source with examples.
7. Define Cnrde drugs, hilum, unorganized dnrg and vittae.
g. Write the botanical source and uses of drugs in which following constituents are present a) diosgenin b) sennosides c) aloe emodin d) emetine.
g. Write tlre chemical tests to identifr pale catechu and agar.
10. What are enzpes? Mention the botanical source, chemical constituents and uses of any one drug containing enzymes.
11l. Describe the imporknt characteristics of umbelliferous fiuits.
12. Distinguish between digtalis and vasaka in their morphological characters.
13. Write a note on swelling factors and nuffiieg mace.
SECTIONB
14. a) Define adultsration and substitution of a) licorice b) vinca c) castor oil
4+10
b) Explain morphological and pharmacological evaluation.
OR
Define and explain a) veinislet number b) stomatal index c) foreign organic
matter d) moisttue content e) ash value f1 loss on drying d paliside rrtio 2X7
15. Explain alkaloids and lipids. 7+6
16 Write tlrc method of cultivation, method of collcction and stonrgc of ugot and digitalis. 7+$
17. Describe ttre anatomical characters of fennel and cinnamon witli &e help of neat diagrams. rr+rr 67
D3300110/9/JAN 2010
DSSI) OIIO GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA
BOARD OF EXAMINING AUTHORITY
D.PHARM, PARTI EXAMINATIONS (ER91) Jan 2010.
Time3 hrs PIIARMACOGNOSY Max, Marla80
NoteAnswer any ten questions from SectionA and any three questions from
sectionB including question No. t4 which is compulsory.
SECTIONA
4xl0 .40
1. Define Phrrmacognosy. Name various classification of crude drygs.
2. Give name, source, family and use of crude dnrg belonging families
a) Apocynadeae b) _Meliaceae
3. Write a note on preparation of surgical catgut
4. Mention fcrur different ways by which a crude drurrs adulterated.
5. Describe chemical tests a) Keller Killiani b) Modified Bomtragers test
6. Give source and use for sample containing Oleoresin and Balsam resin.
Write constituents and uses of a) Isabgol b) Rhubarb
Giveiconstituents and uses. a) Sedative, b) Purgative
Write mprpholggy and constituents of CIovE.
How do you distinguish cotton fiber from wool fibers and sutures from ligatrues.
Mention name, sources, farnily and uses of crude drugs containing
a) Ferulic acid b) Invert sugar
12 What are enzr, ryrrres? Explain collection of Papain.
13. Write a note on natural emulsifying angents
SECTIONB V
14. Whatare oardiac glycosides? pxplain tests for identification. Give
two eg crude drugs containing same and explain any one of them in dehil
OR 2+3+9
Discuss in detail about evaluation of crude drugs 14
15. Mttrlabeled diagram describe macroscopy of Nux vornioa
give its sourse, chemical constituenJs and uses 9+4
16. Describe life cycle of Ergot. Write a note on its cultivation and collection
Give iB uses.
17. Write ehernical tests useful in identification of following
a) Agar b) Gelatin c) Benzoin d) Honey.
. lrrtt 6+5+2 4+3+3+t
D3300610/10/JUN 2010
D33() () 6IO
Note Answer any ten questions frorn SectionA ancl three questions from
SectionB including question No.14 which is compulsory.
diagrams wherever required.
SECTION.A
4xl0 = 40^
I. Llst otrt any four irnportant phytoconstituents and mention one drug for each
type rnith their biological source and use.
2. Give orne example for a drug used as following category and write its active
constiluents. a) Diuretic b) Antileprotic.
3. Define the following
a) Ash value b) Extractive values c) Locatives d) Carminatives.
4 Write organoleptic characters of Myrrh and Tolu balsam
5. Write chemical constittrtents and uses of following drugs
a) lpecac b) Dioscorea.
6. Defme cardiotgnirc and give constituents of any two drugs of same categoryi
7. Describe pharmacological classification of crude drugs with merits and
demerits.
8. Give biological source, chemical constituents and uses of Pterocarpus and Garlic.
Explain microscopical characters of fennel fruit.
Name drug with its chemical constituents used as a) Anticancer
b) Antitussive c) Emetic c) Antiseptic
Explain morphological characters of liquorice root.
Name drug and give its biological source and uses for following
constituents. a) VitaminA b) Eugenol.
Name rmd give constituents of one drug belonging to following family
a) Papaveraceae b) zingiberaceae c) Acanthaceae d) Gneataceae
SECTIONB V
14. Name different methods for evaluation for crude drugs. Explain
organoleptic and physical evaluation with suitable examples. 3+6+5
OR
Describe anatomy of Cinchona and Senna with labelled diagram. 7+7
I5. Write source, preparation and identification tests for the following
a) Alginate fibres b) Wool c) Absorbent cotton 44+5
16. Give the collection and processing of Rauwolfia and Senna 7+6
17. Write short note on a) Solanaceous drugs b) Gums and Mucilage
t+l+
c) oxytocics r+, .r
D3300111/11/JAN 2011
D33OOI I I GOVERTMENT OF KARNATAIG
BOARD OF EXAMINING AUTHORITY
D.PHARM, PARTI EXAMINATI0NS (ER9 l)
Time3 Hrs. PHARMACOGNOSY Max.Marks8O
Notq fursner any ten questions from SectionA and thrce questions from
SectionB inclu, ling question No.l4 which is compulsory.
SECTION.A
4x10=40
Describe morphologrcal characters of Ginger and Rauwolfia.
Name drugs having following pharmacological activity and give its botanical
source and uses. a. Diuretic b. Antiamoebic c. Antiarthritic d. Hypotensive
What are tannins? . Classifr and give examples
Describe chemical tests useful in differentiating Acacia and Tragacanth.
Name and give chemical constituents of any one drug belonging to
a. Apocyanaceae b, Rubiaceae c. Rananculaceae d. Rutaceae,
Write notes on Physical method of evaluation.
Differentiate between senna and digitalis in its morphological characters.
Write a note on separation of volatile oil.
Describe chemical method for classification of crude Crugs and olassis.
Give source and use of the drug containing following consti$tents
a. resinoleic acid b. atropine c. Pyretluin d. Barbaloin.
Discuss tho chemical constituents for ttre following drugs
a. Gelatin b. Kurchi c. Golhru d. Ergot.
Differentiate between sutures and ligatures.
Discuss fastors influenoing the oultivation of medicinal plants.
SECTIONB V
Define adulteration. Classify various methods for adulteration of crude
drugs. Writo notes on microscopicalevaluation of crude drugs. 8+6
OR
Describe microscopyof senna and Ginger with neat labeled diary.
Classify alkaloids with eg. Write tests to identi$ them and method
usoful in separation of alkaloids.
16. Wrirc short notes on a. Phanmaeeutical aids and
5+4+4
b. History of Fharmacoglosy. 71$
17. With neat laMed diagram desoibo morphology of
a. Kuohi b. Ginger c, .Coriander 3+5+S
D3300611/12/JUN 2011
03300611 G0VERNMENT OF KARNATAIG
BOARD O[ EUMINING AUTHORITY
D. PHARM Part I EXAMINIATION (ER91)
Time 3 Hrs PHARMACOGNOSY
Max. Marks80
Note Answer any TEN questions from section A and any THREE from section B, including question No. 14 which is compulsory. Draw neat labeted diagrams wherever required.
SECTION A
4 x 10 = 40 Marks
1. What are surgical dressings? Classify with examples.
2. Define enrymes. Give souroe and uses of any Tn/O enzymes
3. Name a drug, which has following active constituents
a) Vitamin C b) Vincristine c) Strychnine d) Eugenot
4, Define resins. Write their properties and classification with examples.
5. Write differences between volatile oil and fixed oil
6. Define alkaloids. Write the tests to identify alkaloids
7. Deftne dnd classify pharmaceutical aids with exarnples
8. Explain biological evaluation of drugs.
9. Give the biological source, active constituents and uses of
a) Guggulu b) Ghalmoogra oil c) Ginger d) pyrethrum
10. Define a) Stomatal Number b) Sutures c) Ligatures d) Palisade ratio
11. Write a note on saponin glycoside
12. Write identification test for Aloe and Agar
13. Give oficial source, active principles and any two drugs used as laxatiVes
SECTION B v
l0hils
14. Describe microscopical charecters of Clove and Cinchona with help
of e neat hbeled diagram OR g + 6
Write notes on a) Life cycle of ergot b) lndigenous of system of mcdlcine I +T
15. Write cultivation and collection of Oplum and Digitalis 7+6
16. a) Explain different methods of classification of crude drugs wlth aomples
b) Define adulteration and give any live methods of adultenation E + 5
17. Describe morphology of following wlth help of neat lahled diegra1
a) Digltalis b) Nutrneg c) tPecac
tfit
E+4+4
3300612/13/JUN 2012
Diir) 06r2 G0VERNIvIENT 0F KARNATAKA
BOARD OT EXAIVIININC AUTHORITY
D.PHARM. PARTI EXAMINATIoNS (ER9 I )
Timc3lrs pHARMACoGNosy Mar lr4arky80
Note Answer any ten questions from SectionA and three from SestionB
including Question No.l4 which is compulsory.
SECTIONA 4X10=40
I, Name four Iaxative drugs. write source, family and constituents of them
2. Describe the rnorphology with neat labelled_diagram of a) Ookru b) Colchicum
3 Explain principle and procedure involved in deterrnination of ash value
4. Give biological source, farnily, chemicatconstituents and uses of any one drug
containing vitamins,
5. Differentiate between animal and plantfibres
6. Narne and give chemicalconstituents of any one drug belongingto a) Loganiaceae
b) Myristicaceae c) aporynaceae d) Rubiaceae
7,Give the source, family and chemical con$ituents of one antitumour crude drug
8. Describe following chemical tesls a) Borntage/s test b) Gambir fluorescent test
9. Narne drug containing following con$ituents and give its botanical source and uses
a) Brucineb) .Morphine
10. Describe pharmacological classification of crude drugs with merits and demerits
11. Write source, family and constituents of any two drugs obtained frorn animal Source
12. Explain histological characters of Ginger rhizome
13. What are surgical dressings? Give method of preparation of surgical cotton
SECIIONB (
14. Describe anatomical feahrcs of Fennel and Cinnamon with
help of neat tabelled dragmm l+7 0R
Desrih sflrce, familX morphology, active constituents, method of
collection x1fl preparation of opium, 2+4+2+3+3
15. Define evaluation of cnrde d$ mention vuious types of adultemtion of
. crude drugs with examples, add a note on Pharmacopeial standuds. 2+6+5
16. Define Phamacog[osy, explain history and scope of Pharmacognosy. Z+fns
l7 . Discuss Phamacognostic stud of three antidiabetic cnrde drugs 13
D3300113 /14/JAN 2013
1. Write a brief note on Antitussives.
2. Explain following chemical tests a) combined umbelliferone test
b) Modified borntraggers test.
3. Describe morphology of Digitalis and Clove with neat labelled diagram
4. Differentiate between Pale and Black catechu by chemical tests.
5. Give an example each for following categories
a) Suspending agent b) Perfuming agent c) Binding agent d) Demulcent
6. Give source constituents and uses of one drug from following families
a) Rubiaceae b) Leguminosae.
7. What are cardiac glycosides?
8. Describe gross anatomical details of Ginger with neat labelled diagram.
9. Describe cultivation and preparation of Digitalis.
10. Name important chemical constituents of
a) Neem b) Asafoetida c) Aloes d) Cannabis
11. Classify drugs acting on nervous system with examples.
12. Explain chemical method of identification of crude drugs with suitable e.g.
13. Write the botanical source, chemical constituents and uses of opium.
Section B v
14. Describe the source, chemical constituents, uses and life cycle of Ergot.
0R 2+4+2+5 = t
Define Pharmacognosy. Describe history and scope of Pharmacognosy.
Add a note on Ayurveda.
2+3+3+G10
15. Write a note on extraction and purification of a) Alkaloids b) Resins. Z+S=13
16, a) Define volatile oils. Give their distribution,
General properties and methods of separation. B
h) What are lipids? Differentiate between fixed oils and volatile oils. r5=tt
L7. write note on a) Adulteration b) Chemical method of evaluation S+n=fS
c) Tannins. Rirr
D3300613/15/JUN 2013
03300, 613 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA i.
BOARD OF EXAMINING AUTHORITY
D. PHARM., PART t EXAMTNATTONS (ER91)
Time 3 Hrs PHARNIACOGNOSY Max. Marks 80
Note Answer any TEN questions from SectionA and THREE from Section B
including Question No. ld which is compulsory.
SECTIONA 4X10=40
1. Explain morphologicalclassification of crude drugs.
2. Define enzymes. Give source and uses of diastase and yeast.
3. Write the botanical source and c c for the following drugs
a) Myrrh b) Gokhru c) Guggul dlVasaka.
4. Describe cultivation and collection of opium.
5. Define tannins and give its identification tests.
6. Give source, uses, of drugs containing following c c
a) Anethole b) &Linalol c) Brucine d) Aimalicine.
7. What are surgicaldressings and give method of preparation of cotton.
8. Describethe different methods of adulteration of crude drugs.
9. Describe important characteristlcs of umbelliferous fruits.
10. Name a drug belonging to following families and glve source uses
a) Lauraceae h) Plantaginaceae clMyristicaceae dl Rubiaceae.
11. Describe following tests a) ModSfied Borntiage/s test
b) Cornbined umbelllferone test.
t2. Give one eg drug used for following category and write its
source and chemlcalconstituents a) Antimalarial b) Antirhematic
13. Name any two crude drugs obtained from animal source,
mention their source, family, chemicalconstituents and uses.
sEcnoil B
14. Describe anatomlyof Cinchona and Sennawith neat hbelled diagram,
OR 7+V
al Define drug ewluation and elasslfy them wlth examples.
b) Explaln physicaland chemical evaluation. 4+10
15. Write noteson a) Pharmaceuticalaids b) Hlstoryof Pharmaoogmslr
cl Ayurvedic. System of Medicine t[+5. 4
16. a) What are glycosides?
Give their properties and classifo them with snita, ble examples. t+l
b) Name the source and chemicalconstituents and
uses of any tulo s@ntn gly, cosides.
17. What are alkaloids? Claseitythem wlth examphs. Explain the rnethodu
to extrast alkaloids and Elvethemiealteststo identifythem.,t
D3301213/16/DEC 2013
D33ou13 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA
BOARD OF EXAMINING AUTHORITY
D. PHARM., PARTl Examinations (ER91) December2013
PHARMACOGNOSY
Time 3 Hrs Max. Marks 80
Note Answer any TEN questions from SectionA and THREE from Section B including
Question No. 14, which is compulsory.
Section A 4x 1o40
1. Write a brief note on scope of Pharmacognosy.
Z. Explain the following chemical tests a) Keller Killiani Test b) Goldbeaters Skin Test.
3. Describe the morphological characters of a) Senna b) cinchona
4. Differentiate between Gums and Mucilage’s.
5. Give one example each for following categories
a) Flavouring agent b) Emulsifier c) Disintegrating agent d) Colouring agent.
6. Give botanical source, chemical constituents and uses of
One drug each from following families a) Liliaceae b) Labiate
7. Explain saponin glycosides.
8. Explain the process of preparation of surgical cotton.
g. Explain in detail gross anatomical details of clove with a neat labelled diagram.
10. Name important chemical constituents of a) cinchona b) Ginger c) Vinca d) Colchicum.
11. Write a note on drugs used as antidiabetic with source and active principles
12. Write a note on solanaceous alkaloids with source and uses.
13. Write the botanical source, preparation and uses of ergot.
SectionD
14 Define crude drug adulteration.
Explain different means of adulterating crude drugs with examples. 7
Describe the microscopy of fennel with the help of neat labelled diagram +?
OR
Define crude drug evaluation. Explain microscopic and organoleptic methods of
Evaluating crude drugs with merits and demerits. f4
15. Write a note on a) Glycosides b) Tannins. 7+6
16. A) Define alkaloids. Give their distribution, general properties and identification test.
$, Explain the source and methods of collection of Senna. t1i6
rt. writes notes on
a) Antiseptics and Disinfectants b) Natural fibres c) cardiac glycosides. 5+t
r.r1.
D3300414/17/APRIL 2014
D3300414 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA
BOARD OF EXAMINING AUTHORITY
D. PHARM., PART l EXAMINATIONS (ER911. AprilZ014
Time 3 Hrs PHARMACOGNOSY Max. Marks 80
Note Answer any TEN questions from SectionA and THREE from
Section B including Question No. 14, which is compulsory.
sEcfloN A 4Xl0 40
l. Define diuretics. Name two diuretic drugs and give their botanical source
2. Define and classifr Pharmaceutical Aids with examples.
3. Write official sources, active constituents of
a) Nutmeg b) Clove c) . Tolu balsam d) fennel.
4. Define a) Adultenation b) StomaQl number c) Palisade ratio d) Crude drug.
5. Define alkaloids. Write the test to identify alkaloids.
6. Name and give chemical constituents of any one drug belonging to
a) Rubiaceae b) Liliaceae_c) Papaveraceae d) Apocyanaceae.
7. Write the method of cultivation and collection of Rauw6lfia,
8. Write a note on Tannins.
9. Name drug _a0d give its botanical source and uses for
following constituents a) Emetine b) $rethrine c) Nicotine Q Monttrol.
10. Draw a labelled diagram tbr the rnicroscopical eharacters of ginger.
I l. Write chemical tests for acacia and pale catechu.
12. Describe pharmacological classification of srude drugs.
13. Explain morphological evaluation oforude drugs.
SECTION. B V
14. a) Describe soureg cs, morphologyrmethod of
cultivation, colloction of digiAlis. b) Writo a notc on enzynes $s
Write noto on i) perfumes and flavours OR
ii) sutures iii) surgical drcsings. 6++
15. Explain moryihology of a) Gokiru b) Coriander c) Ntlxvomica. S+4+4
16. a) Doffne and olassify glyeosides with examplos. 7+0
b) Writ€ test to identify differenttlpes ofglycosides.
17. a) Explain dlfforent msfiods of aduitenation of drugs . 7+6
b) Add a note on history ofPharmaoognosy.
D3301214/18/DEC 2014
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA
D330 l2l4 (BoARD oF ExAMtNtNG AUrHoRtry)
D. Pharm. Part I Examinations (ER91),December2014
Time 3 Hrs PHARMACOGNOSY Max. Marks80
Note Answer any TEN questions from section A and THREE from Section B
including Question No. 14 which is compulsory
SEgflONA 4X10=40
1. Describe chemical classification of crude drugs with merits and demerits.
2. Give biological source, chemical constituents and uses of Pyrethrum and Tobacco.
3. Give official source and uses of drugs containing the following active principles
i) Santolol, ii) Azadiractin iii) Quinine iv) Commiphoric acid
4. Describe morphologicalcharaEters of Ephedra and Aconite.
5. Give differences between organized and unorganized drugs.
6. Give biological source, chemical constituents and uses of
Shankapuspi and Linseed.
7. Describe chemical tests for Agar and Tragacanth.
8. Describe microscopical characters of Ginger.
9. Give name biological source and uses of any one drug belonging to the following
families IlPolygoraceae, ii) Plantaginaceae, iii) Combretaceae and iv) Lauraceae
10. Describe modified Borutrage/s test and Vitali Morins test.
11. Give the biologicalsource, chemical csnstituents and uses of Tolu Balsam and Tuisi.
12. Give one example for each of the following with their uses
i) Fungus, ii) Latex, iii) Juice A iq Rhizome
13. Give the biological sources, chemical constituents and uses of
Ashwagandha and Dioscorea,
sEcnoN B v
14. A) Define adulteration, give different methods of adulteration of crude drugs
B)Write a short note on indigenous system of medicine 7 + 7 = 14
OR
Al Describe morphological and microscopical character of Cinchona bark
B) Write short note on surgical dressings 7 + 7 = t4
15. Write notes on Oxiocic i) Drugs containing reslns iii) Antidiabeitc drugs S +4+ 4 = t3
16. Describe methods sf collectioh and preparation of Opium and Senna. T + E = 13
17. Describe morphological and microscopical characters of ipecac trdtrh 51t =13
neat labelled diagram
D3301215/19/DEC 2015
D3301215
Time 3Hours
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA
(BOARD OF EXAMINING AUTHORITY
D. Pharm. Part I Examinations (ER91) December20L5
PHARMACOGNOSY
Max. Marks 80
Note Answer any TEN questions from Section A and THREE from Section B including
Question No. 14, which is compulsory.
Escalon A 4XtO=40
1. Give one example for each of following write their biological source and uses.
a) Rhizome b) Fungus c) Kernel d) Latex
2. Name a drug which has the following constituents a) Emetine b) Glycyrrhizin c) Nicotine d) Hydnocarpic acid
3. Name any two antiseptic drugs and give its biological source, family, Chemical constituents and uses
4. What are resins? Classify them with examples.
5. Give the difference between essential oil and fixed oils.
6. Name a drug which is used as the following along with their source a) Colouring agent b) Diuretics c) Antidiabetics d) Antihypertensive
7. Describe the morphological characters of Ginger and Senna.
8 Write the chemical constituents and uses of the following drugs a) Aconite b) lspagulla c) Shatavari d) Amla
9. Write the biological source, family chemical constituents and uses of Tolu balsam and Honey.
10. Write a note on Pharmacopoeial standards of purity of crude drugs.
11. Give the identification tests for silk and wool.
12. Name any two Pharmaceutical Aids and give its biological source,
Family, chemical constituents and uses.
13. Name any two crude drugs containing anthracene glycosides and
Quinoline alkaloids and give its biological source and uses.
SECTION B
14. Describe the anatomical characters of clove and fennel with the help
Of a neat labelled diagram. 7+7
OR
Explain the cultivation, collection and processing of Digitalis and Rauwolfia 7+7
15. Write notes on a) Natural pesticides b) Terpenoids c) Biological evaluation lt4+S
16. Give the chemical tests for a) Alkaloids b) Cardiac glycosides c) Honey it64
17. Define and explain.
a) Veinislet number b) Foreign organic matter c) Ash value
d) Moisture content e) stomata number f) Adulteration. 2+r+2+2+2+il
D3300416/20/APR 2016
4Xt0
Section –A 4x10=40
1. Give the name and active constituents of any one drug belonging to the following category
A) Cardiotonics b) Antileprotic c) Antitussive d) Flavouring agent
2. Define and classify Tannins with suitable examples.
3. Explain morphological classification of Crude drugs with suitable examples.
4. Write a brief note on scope of Pharmacognosy.
5. Explain the following tests a) Combined Umbelliferone b) Modified Borntrager’s test
6. Write notes on Diastase and Papain.
7. Write the source, preparation and uses of Cotton.
8. Describe the morphology with a neat labelled diagram for a) Nuxvomica b) Fennel
9. Write the name and active constituents of any one drug belonging to the following families
a) Papaveraceae b) Rutaceae c) Apocyanaceae d) Rubiaceae
10. Describe life cycle of Ergot.
11. Give the biological source and therapeutic effect for the following
a) Shankhapushpi b) Colchicum c) Shatavari d) Liquorice
12. Write the differences between Black catechu and Pale catechu.
13. Write the biological source and chemical constituents for Ashwagandha and Cannabis.
SECTION B
14. Define evaluation. Name the different methods of evaluation. Discuss morphological and
Microscopical evaluation with suitable examples, 2+2+5+5
OR
a) What is Adulteration? Write a brief note on different types of Adulteration
b) With the help neat labelled diagram, describe the microscopy of Cinnamon bark. 7+7
15. Write short notes on a) Volatile Oils b) Resins 7+6
16. Write the method of cultivation, collection and preparation of opium and Digitalis 7+6
17. Write short notes a) Natural Pesticides b) History of Pharmacognosy c) Pharmaceutical aids 4+5+4
D3300517/21/MAY 2017
03300517 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA
(BOARD Ot EHMINING AUTHORITYI
D. Pharm. Part I Examinations (ER91),May 2017
Time 3 Hrs PHARMACOGNOSY Max. Marks 80
Note Answer any TEN questions from Sectlon A and THREE from Sectlon B
including Question No. 14, which is compulsory
SECIIONA 4Xt0=40
01. Define Pharmacotnosy and explain Scope of Pharmacognosy.
02. Give name Chemical constituents of one drug belonging to following
category. a. Antileprotics b. Antitussive c. Cardiotonic d. Antidiabetic.
03. Explain Morphological classification of Crude drugs with examples.
04. Describe important characteristics of Umbelliferous Fruits.
05. Describe following tests
a. Combined Umbelliferone test b. Borntrage/s test.
06. What are Tannins? Give ldentification tests for Tannins.
07. Write significance of Pharmacopoeial standards.
08. Define Enzymes. Give source and uses of Diastase and Yeast.
09. What are Pharmaceutical aids? Classify with examples.
10. Discuss the Extraction methods for Alkaloids.
11. Give name, source and uses of any One drug belOngs to tollowlng
families. a. Euphorbiaceae b. Myrtaceae c. Apocyanaceae d. [oganiaceae
12. Describe the cultivation and collection of Opium.
13. Name TWO drugs from animal source. Mention its official source and uses.
SECTION B
14, a. Describe life cycle of Ergot
b. Mention Chemical constituents and uses of Ergot
c. Write a note on any TWO indigenous system of midicine. 6+3+5=14
OR
a. What is Adulteration of crude drugs? Give the different types with examples.
b. Explain Chemical and Biological Evaluation. 7+7=14
15. Give morphology and microscopy of Fennel with neat labeled diagrams.
5+&13
16. a. What are Glycosides? Give properties and classif, y with suitable e8.7+6=13
b. Name the source, chemical constituents and uses of any two Vitamin drugs.
17. Write note on a. Cotton b. Wool c. Regenerated fibers. 5+4+4=13
D3301217/22/DEC 2017
D3301217 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAT
(BOARD OF EXAMTNTNG AUTHOR|1T)
D. PHARM. PAIIT I EXr1F"IINATIONS (ERrgi),DECEMBEII 3C17
PHARMACOGNOSY
f/lax. Marks80
Time3Hours
Note Answer epenyi"EFl questions from Section A and THREE from Section B Including
Question No. 1tl, which is compulsory
1. Define and write Historical drvetopment of Pharmacogirosy.
2. Explain Chemical classification of crude drugs with rnerits and deinerits.
3. Differentiate Organised and Unorganised Crude drugs with examples.
4. Mention TWO crude drugs containing Gums and Mucilages.
5. Give TWO examples each.for IATEX and RHIZOME and write their uies.
6. Name TWO crude drugs belonging to APOCYANACEAE and LILIACEAE along v, rith their active constituents.
7. Give the Official Source and Active constituents of BENZOTN and GARLIC
8. Mention TWO Carminatives with Biological source and Chemical constituents
9. Give TWO identification tests for AGAR
10. Give the name and active ingredients of any ONE crude Drug belonging ts following
category a. Hypolipidemic b. Purgative c. Emetic d. Expectorant
11. Explain a. Keller Killiani test b. Combined Umbelliferone test
12. Name the Bark showing sclereids/stone cells with Biological soLlrce, Aciive constituents and uses.
13. Give the Source and Method of Preparation of Adsorbent Cotton
SECTION.B
14. a. Define Tannins. Classify them with examples. Write the methods of extraction of tannins
b. Give the life cycle of ERGOT 77=14
OR
Explain Physical Chemical and Biological Evaluation of Crude Drugs 6+4.414.
15. a, Define i). Palisade Ratio ii). Vein islet Number iii). Stomata number
b. Define Adulteration and give the different types of Adulteration et7=Ll
16. Explain the Morphology and Microscopy of GINGER and CLOVE G+7=13
17. Write short notes on a. pharmaceutical aids . b. Antidiabetic Drugs 6+7=13
D3300619/23/JUN 2019
D3300619
Time 3 Hours
htrote Answer any
GOVERNMENT OF KARN, A.TAKA
(BOARD OF BXAMINING AUTHORTT9
D Pharm. Part I Examinations (ER91),JL|NEJOI9
PHARMA..GNSY Max Marks 8o
TEN questions from Section A and THREE questions from Section B
Question No 14 is compulsory.
SECTION.A
(4X10=40)
1. Define glycosides. Write a note on Cardiac glycosides.
2. What are Diuretics? Write the Biological Source, Chemical Constituents and uses of any TWO
Diuretic drugs.
3. Explain cultivation and collection of RAUWOLFIA.
4. Give the source and uses of drugs containing following active constituents.
alCepheline b) Ricinoleic acid clPiperine d) Curcumin
5. What are sutures? Give the method of preparation of surgical catgut.
6. Write a note on the general chemical testsTor Black and Pale Catechu.
7. Define Extractive value. Mention different types with their significance.
8. Define the following a) Pharmacognosy b) Drug adulteration
9. Write a note on Vitamines.
10. Define and give examples for following uses.
a) Carminatives b) Antidiabetics c) Antitumors d) Asrtingents
11. Write and explain chemical tests for HONEY and GELATIN (any TWO for Each drug) .
12. Explain the morphology of EPHEDRA and SENNA with diagrams.
13. Differentiate plant fibres and animal fibres with suitable examples.
SECTION _B
14. a) Mention various systems of classification of crude drugs. Explain any TWO methods of
classification of crude drugs.
b) Define drug evaluation. Explain Physical evaluation. (2+5+2+4=141
OR
a) Explain Morphology and Microscopy of CORIANDER with neat labeled diagrams
b)Write a note Hlstory of Pharmacognosy. (2+6+5=14)
l5. a) Write a note on volatile oils.
b) Explain the Pharmacognosy of ERGOT including its Life cycle.
( 5+8= 13 )
16. What are Pharmaceutical aids? Explain in detail any 3 drugs used as pharmaceutical aids.(13)
17 . a) Explain Homeopathic system of medicine.
b) Write a note on Antileprotics.
c) Describe Solanaceous drugs.
(5+4+4=13)
D3300120/24/JAN 2020
D33OO1IO GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA
(BOARD OF EXAITflN|NG AUTHORITYI
D. Pharm. Part - I Examtnrtlonr (ER-91), Jrnuary-2020
PHARMACOGNOSY
Time:3Hours Max. Ma*r: 80
Note: Answer anyTIN questlons from Sectlon -A ond THREE from Scctlon - B lncludln3
Questlon No. 14, which is compulsory
SEGTION -A l1tQ r 40
1. Name sf the drug containlng followlng activc princlple, wrlte lts B.S end uses
a) Qulnine b)Vitamin-C c) Catechln d)Vlncrltlne
2. Give the Chemicaltests for Tragacanth and Benroin
3. Write briefly hlstory of Pharmacognosy.
4. Describe the following tests:-
a) Modified Borntragger's test
b) Fiehe's test
5. Define Resins. Give the classificatlon of Resins with examples.
6. Write the B. $ famlly and therapeutic uses of Papain and Diastase.
7, Describe cultivatlon and Collection of Senna.
8. Differentiate plant fibres and animalffbres with examples.
9. Explain basic principles involved in Ayurvedic system of medlclne.
10. Give one example for each of the following with chemlcals constituents and uses.
a) Dried latex b) Dried Bark c) Kernel d) Fungus
11. Explain Pharmacological Classiflcatlon with ercmples.
12. Write the Morphological of Coriander and Nunrornica with neat labelled dlagram.
13. Give the B. S and method of prepantlon and uses of Sllk.
SECTION -B
14. A.l) Define Drug evaluation. Mention different methods of Evaluation.
.b) Define Alkaloids. Write Properties and Classification of alkaloids
(2+3t2+2+5)
OR
B. a) Write a note on the perfumes and flavouring agents.
b) Explain the Morphology and microscopy of Clnnamon bark wlth neat labelled
diagram. (0 + g)
15. a)Write a note on TerPenoids.
b) Explain Pharmacognosy of the two Diuretic. ( 4 +91
16. a) Cultivation and collection of Dlgitalis
b) Write a Chemicals tests for Cardiac Glycosides
c) Explain Organoleptical evaluatlon. l{ + 5 +tt}
17. a) Chemicals tests for Black and Pale Catechu
b) Write a note on Antiseptics.
c) Gums and Mucllages rrrr. lif + S + Q
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)